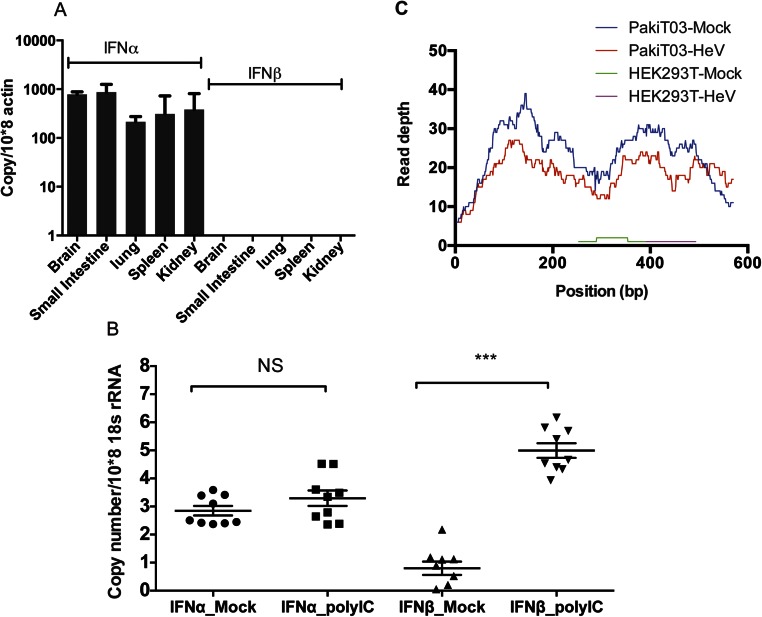
Fig. S3.
Bat IFN-α has a constitutive and ubiquitous expression pattern. (A) qRT-PCR detection of IFN-α and IFN-β mRNA expression in five C. brachyotis tissues (n = 2). The expression level was normalized to housekeeping gene actin. The error bars represent SD. (B) Expression of IFN-α and IFN-β mRNA following polyI:C stimulation of bat primary cell lines. The primary cells include lung, liver, heart, kidney, small intestine, brain, fetus, salivary gland, and muscle. Data represent the mean and SE of duplicates from each cell line. Two-sample t tests for unequal variances were used to compare the treated and mock-treated samples. NS, nonsignificant (***P < 0.001). (C) The transcription profile of IFN-α in PaKiT03 and HEK293T cells in mock samples or 8 h following HeV infection. Data show read counts per nucleotide for IFN-α.