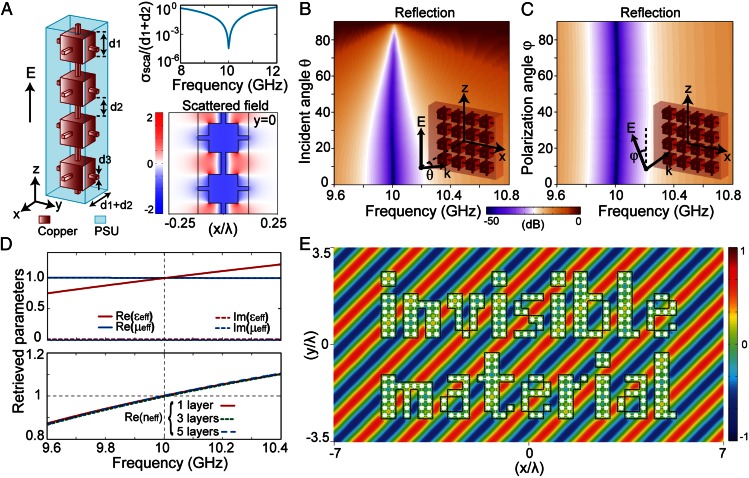
Fig. 2.
Numerical results of the invisible material made of corrugated metallic wires. (A, Left) Geometry of a modified wire, composed of corrugated conducting square wire embedded in a dielectric with εr = 3 and a loss tangent of 0.0013. (A, Top Right) Normalized scattering width (5 10−5 at 10 GHz) under a normal plane-wave incidence along the x axis with the unit-amplitude electric field polarized along the z axis. (A, Bottom Right) Scattered electric field around the corrugated wire at 10 GHz. (B) Simulated reflectance spectra (S11) for one layer of wires with respect to the angle of incidence. (C) Simulated reflectance spectra with respect to the polarization angle. (D) Retrieved effective parameters of the solid slab composed of closely arranged corrugated wires with different layer thickness. For the one-layer slab, εeff = 0.9999 + 0.006i, μeff = 1, and the refractive index neff ∼ 1 + 0.003i at 10 GHz. (E) Steady-state electric field distribution under an oblique plane-wave incidence at 10 GHz upon an invisible material-shaped structure composed of the designed wires. The electric field is polarized along the z axis.