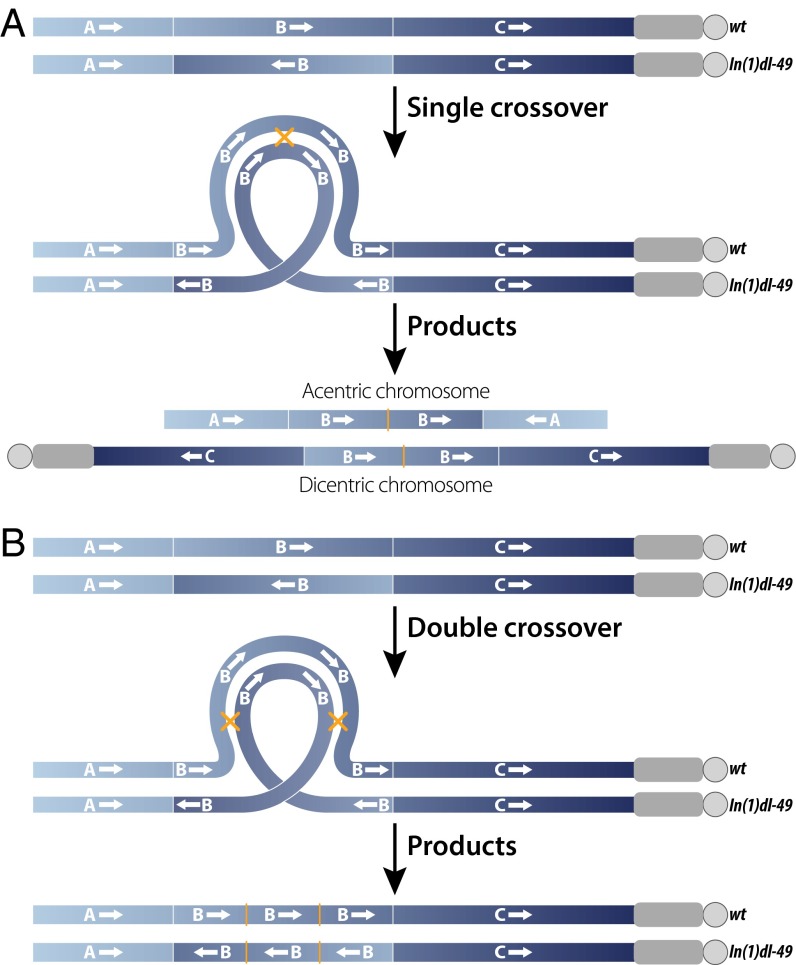
Fig. 1.
Consequences of a single or double crossover between a WT X chromosome and an X chromosome carrying a single inversion, In(1)dl-49. Euchromatin is shown in blue, heterochromatin is shown in gray, and centromeres are depicted as circles. Thin white lines mark locations of inversion breakpoints, and yellow crosses/thin lines mark locations of crossover events. (A) A single crossover event within the inverted segment results in the formation of chromosomes with deletions and zero (acentric) centromeres or duplications and two (dicentric) centromeres, neither of which will segregate properly during meiosis. (B) A double crossover within an inverted segment results in intact chromosomes with one centromere that will segregate properly during meiosis.