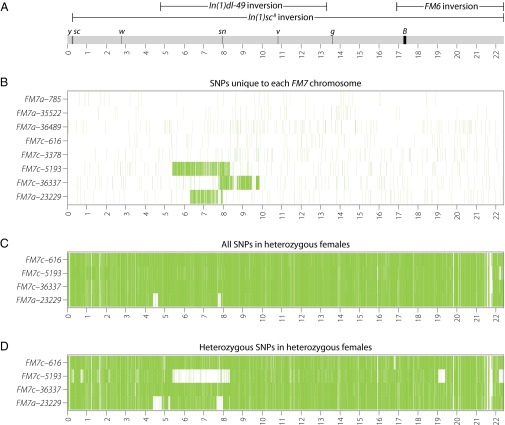
Fig. 3.
Recombination generates sequence diversity among FM7 balancer chromosomes. (A) Schematic of the WT X chromosome showing the locations of inversions (oriented with respect to the reference genome, not FM7), visible genetic markers, and Release 5 genome coordinates (in Mb). (B) Heatmap of unique SNPs found in only one FM7 chromosome in our sample. The density of unique SNPs is plotted in 5-kb windows with a 5-kb offset. The three large tracts of unique SNPs on FM7c-5193, FM7c-36337, and FM7a-23229 are contained fully within In(1)dl-49 and replace the snX2 allele with the WT sequence. The FM7a-23229 chromosome is a mislabeled FM7c (Fig. S1B). (C) Heatmap of all SNPs found in heterozygous female samples carrying FM7 balancers over different balanced X chromosomes. Genotypes of balanced X chromosomes are listed in Dataset S1. Small tracts in which few SNPs are present in FM7a-23229 arise because of common ancestry among the X chromosomes in FM7, the balanced chromosome, and the ISO-1 reference genome (Fig. S1C). (D) Heatmap of heterozygous SNPs found in heterozygous female samples carrying FM7 balancers over different balanced X chromosomes. LOH is observed for a large tract in FM7c-5193 that corresponds to the large tract of unique variants for this chromosome shown in B. LOH is also observed in FM7c-5193 for two deletions in the balanced chromosome [Df(1)JA27 and an uncharacterized deletion on the Df(1)JA27 chromosome], and for tracts in FM7a-23229 that share ancestry with y1-ncdD and ISO-1 (Fig. S1C).