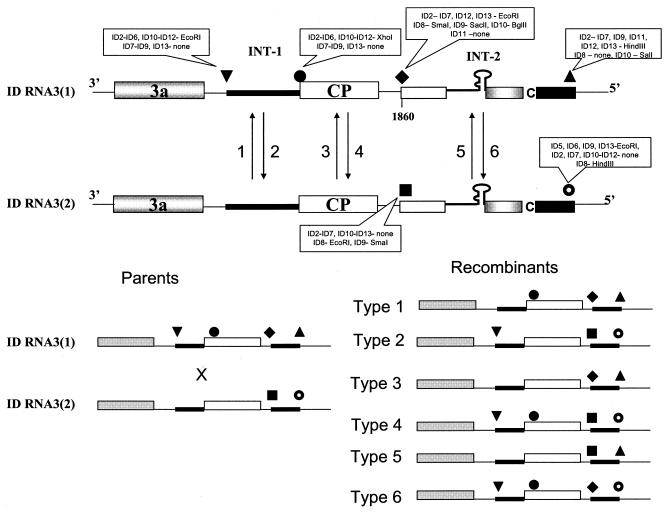
FIG. 2.
General illustration of homologous crossovers occurring between two coinoculated variants of ID RNA3s. At the top, the regions of sgp-mediated crossovers at the INT-2 locus, the INT-1 locus, and the control CP ORF are shown schematically (not to scale). The elements of the RNA3 molecule are represented as in Fig. 1; arrows indicate homologous crossovers. The types of ID RNA3s carrying specific restriction sites at four restriction marker positions (indicated by circles, triangles, diamonds, and inverted triangles) are given in the balloons (see also the restriction marker table in Fig. 1, right side). Below the crossover schematic, the molecules of two parental ID RNA3 variants [designated generally as ID RNA3(1) and ID RNA3(2)] are shown on the left, whereas the predicted types of progeny RNA3-RNA3 recombinants that arise due to crossovers within the recombination regions (see also Table 1) are shown on the right. Solid rectangles, INT-1 and INT-2 regions; shaded and open rectangles, ORFs.