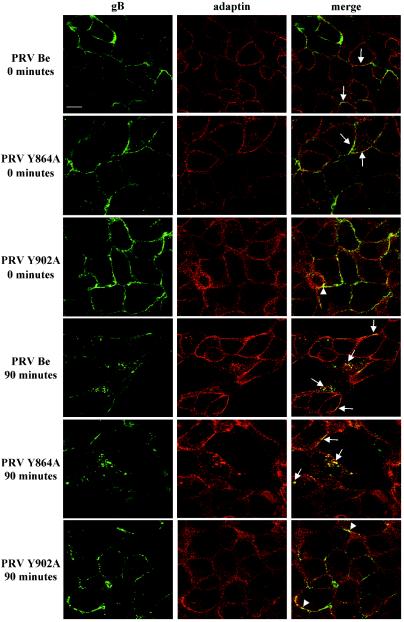
FIG. 2.
Colocalization between gB and α-adaptin in PRV-infected cells. PK15 cells were infected at an MOI of 10 with either PRV Be, PRV Y864A, or PRV Y902A. All infected cells were processed for an antibody-dependent internalization assay and stained for gB (left column) as described in Materials and Methods. Internalization was allowed to proceed for 0 or 90 min at 37°C. Thereafter, the cells were costained for α-adaptin (middle column). To this end, the cells were incubated with monoclonal anti-α-adaptin IgG1 antibodies (clone AP-6), biotinylated rabbit anti-mouse IgG1-specific antibodies, and streptavidin-Texas Red. Merged images (right column), obtained by superposition of the green (gB) and red (α-adaptin) stainings, indicate areas of colocalization (yellow) between PRV gB and α-adaptin. The arrows indicate colocalization between wild-type or Y864A gB and α-adaptin in cytoplasmic internalization vesicles or at the cell surface, whereas the arrowheads indicate colocalization between Y902 gB and α-adaptin at the cell surface. Bar, 10 μm.