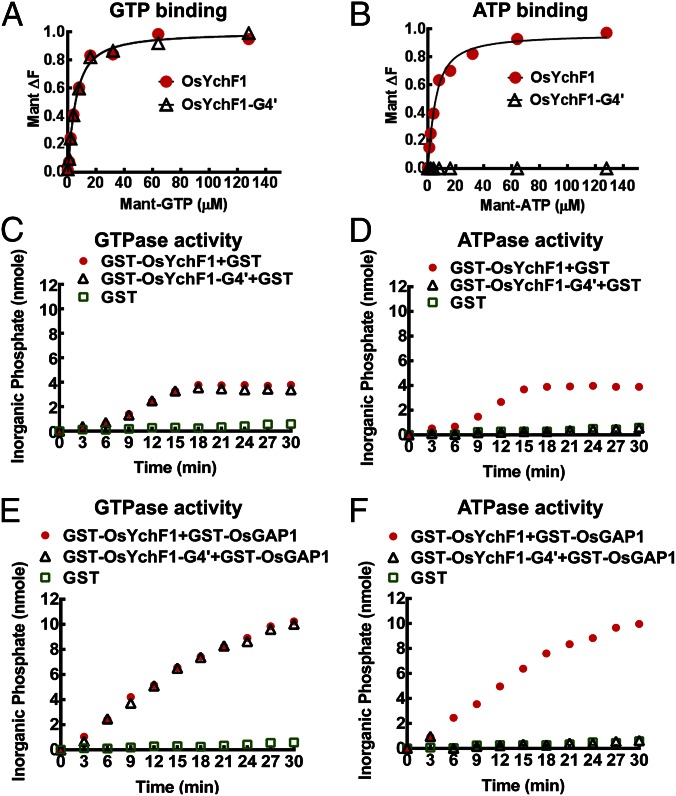
Fig. 3.
GTP/ATP binding and GTPase/ATPase activities of OsYchF1 and OsYchF1-G4′. (A and B) OsYchF1 and OsYchF1-G4′ were titrated with Mant-GTP (A) or Mant-ATP (B). GST-OsYchF1 and GST-OsYchF1-G4′ fusion proteins were expressed in E. coli, purified, and the GST tag was removed before the titration experiments. The final concentration of the target protein in the binding assays was approximately 6.5 µM. Emission signals were collected at a wavelength of 445 nm. For both A and B, circles, OsYchF1 protein; triangles, OsYchF1-G4. Data fitting was performed by using Prism 6.01v (GraphPad Software). OsYchF1 was able to bind both ATP and GTP with similar affinities, whereas OsYchF1-G4′ was only able to bind GTP. (C–F) The hydrolytic powers of GST-OsYchF1-G4′ and GST-OsYchF1 toward GTP were comparable (C), but only GST-OsYchF1 could hydrolyze ATP (D). GST-OsGAP1 could further enhance the GTPase activity of both GST-OsYchF1-G4′ and GST-OsYchF1 (E), but could only enhance the ATPase activity of GST-OsYchF1 but not that of GST-OsYchF1-G4′ (F). GST controls did not exhibit either GTPase or ATPase activities. For C–F, circles, GST-OsYchF1 protein; triangles, GST-OsYchF1-G4; squares, GST only.