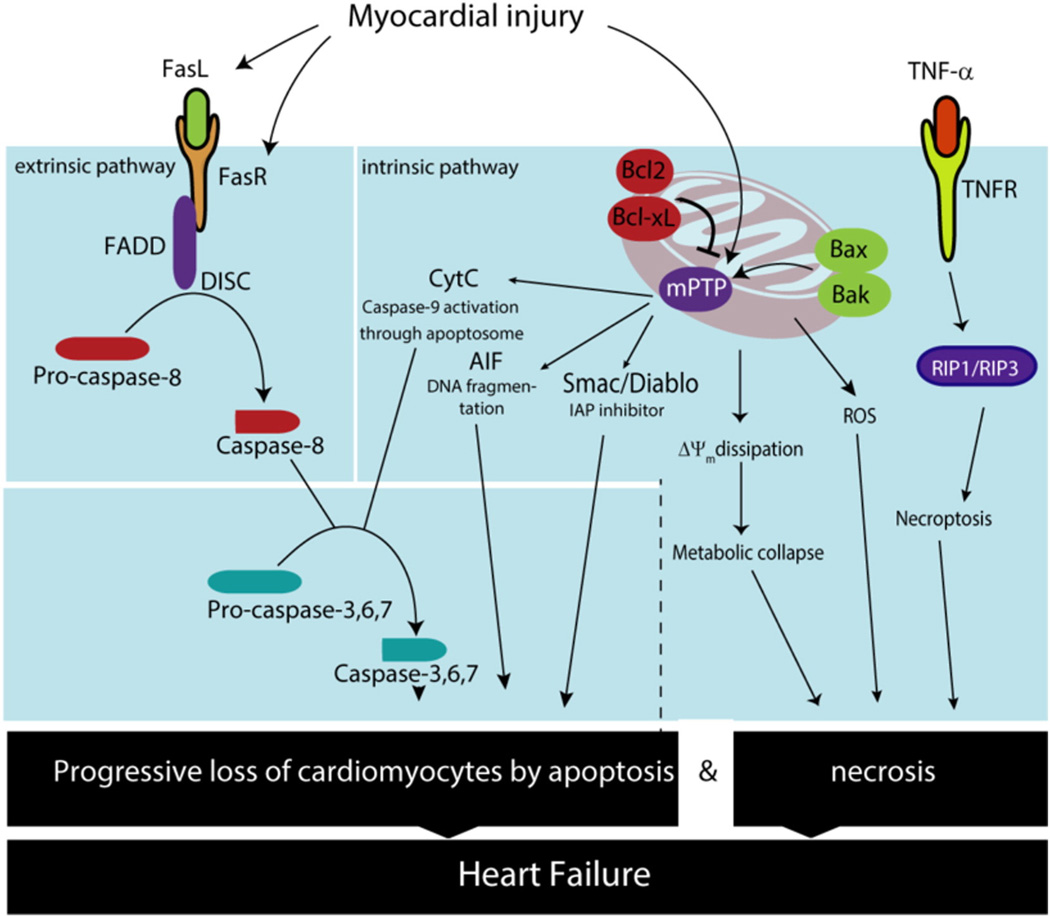
Fig. 3.
Increased levels of apoptosis and necrosis are observed during HF. Activation of both the extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways have been described in HF. Activation of FasR leads to caspase-8 activation and extrinsic pathway activation. On the other hand, mitochondrial permeabilization leads to cytochrome C, AIF and Smac/Diablo release, which triggers the intrinsic pathway. Similarly, mitochondrial Ca2+ overload leads to mitochondrial membrane potential dissipation (ΔΨm) and ROS production, which ultimately trigger necrosis. In addition, regulated necrosis or necroptosis has emerged as another source for cell death in HF through activation of RIP1/RIP3. Over time, cardiomyocyte death results in a decreasing abundance of functional cardiomyocytes in the failing heart, which further deteriorates cardiac function.