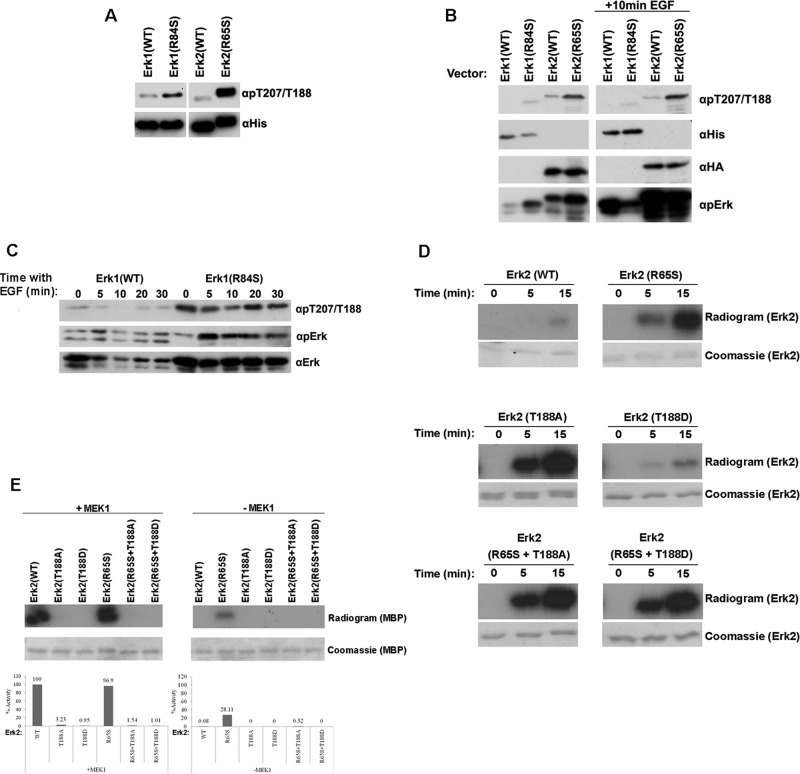
FIGURE 6:
The active variants Erk1(R84S) and Erk2(R65S) are autophosphorylated at a novel phosphoacceptor, T207 (in Erk1) and T188 (in Erk2), which is critical for catalytic activity. (A) The indicated Erk proteins (recombinant purified) were subjected to Western blot analysis, using antibodies specifically raised against phospho-Thr-207/Thr-188 (αpT207/T188) and anti-polyhistidine antibody (αHis). (B) The indicated ERKs were introduced into HEK293T cells. At 48 h posttransfection, cells were serum starved for 24 h. Then cells were exposed or not exposed to 50 ng/ml EGF for 10 min, harvested, and subjected to Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. (C) Phosphorylation of T207 in Erk1(R84S) is not affected by EGF. NIH3T3 cells stably expressing Erk1(WT) or Erk1(R84S) were collected, and protein lysates were prepared at the indicated time point after EGF addition. Cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. (D) Erk2(T188A), but not Erk2(T188D), manifested dramatic increase in autophosphorylation activity. Autophosphorylation of purified Erk2(R65S), Erk2(T188A), and Erk2(T188D) was tested by incubating the proteins in a kinase assay mixture with [γ-32P]ATP and no other substrate. Samples were removed from the assay at the indicated time points and subjected to SDS–PAGE. Gels were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue, dried, and exposed to x-ray film. (E) Mutating T188 of Erk2 to either Asp or Ala diminished its catalytic activity. Catalytic activity of the indicated protein was assayed as described in the legend to Figure 5.