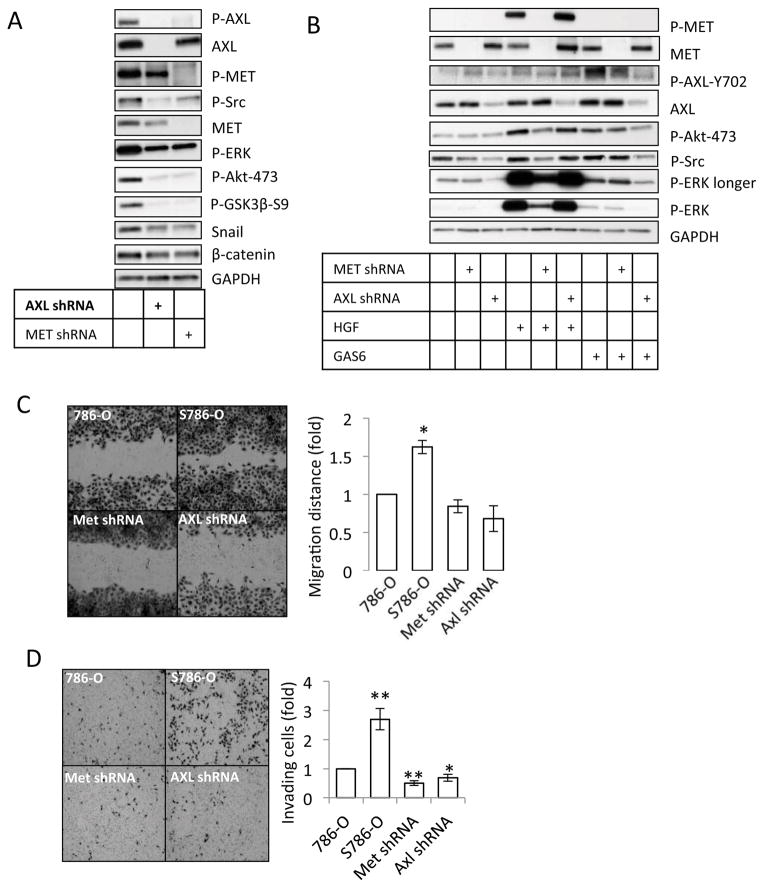
Figure 3. Chronic sunitinib treatment induced EMT is AXL and MET dependent.
(A) 786-O cells, 786-O cells that stably expressed AXL or MET shRNA constructs were chronically treated with sunitinib (1 μM) and then deprived of sunitinib for 48 hours. The cells were examined by western blot with specific antibodies as indicated. Data represent three independent experiments. (B) Chronic sunitinib pre-treated cells (786-O, AXL shRNA, and MET shRNA) were deprived of sunitinib for 3 days. The cells and 786-O parental cells were then serum starved for 24 hours followed by HGF (100ng/ml, 30minutes) or GAS6 (200ng/ml, 30minutes) stimulation as indicated. The cells were then lysed and examined by western blot with specific antibodies as indicated. Data represent three independent experiments. (C). 786-O cells, 786-O cells that were stably infected with AXL or MET shRNA constructs were chronically treated with sunitinib (1 μM) and then deprived of sunitinib, and 786-O parental cells were seeded for wound-healing experiment as described in Methods. The gap distances in four independent experiments were measured and analyzed. (D). The transwells were coated with Matrigel as described in Methods. 786-O cells, 786-O cells that were stably infected with AXL or MET shRNA constructs were chronically treated with sunitinib (1 μM) and then deprived of sunitinib, and 786-O parental cells were seeded (10, 000 per well) in the transwells in serum free medium. Complete Growth Medium was added to the bottom wells. After 24 hours, the invading cells were stained and counted as described in Methods. The data in this figure is representative for 3 shRNA constructs designed to target different sequences in MET and AXL.