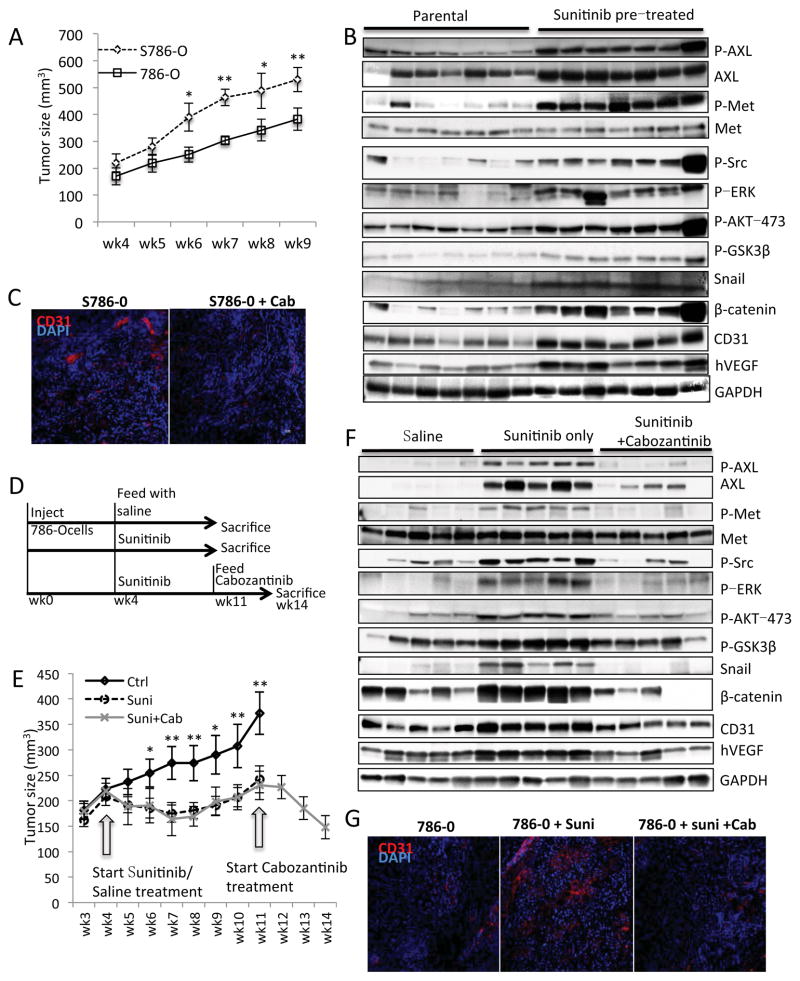
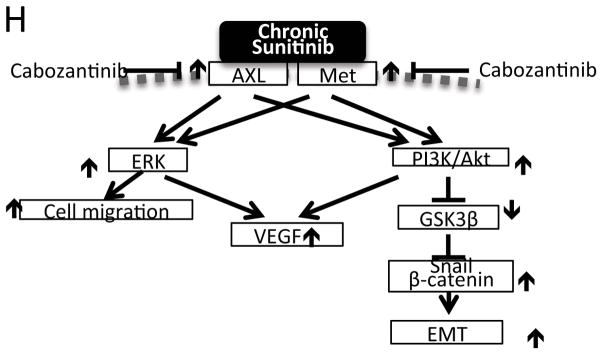
Figure 6. Chronic sunitinib treatment induced AXL and MET signaling and angiogenesis in xenograft mouse models.
(A) 1x107 786-O cells (786-O) or chronic sunitinib pre-treated 786-O (S786-O) were injected into the flank of each NCr-nu/nu mouse (10 mice per group). The xenograft tumor sizes were measured after 4 weeks’ stabilization. The size difference between two groups at same time point was analyzed using the Student t-test. (* indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.01). (B) The mice were sacrificed after 9 weeks, the tumor tissue was obtained and equal amounts of protein lysate were analyzed by western blot with specific antibodies as indicated. (C) Representative immunohistochemistry staining of CD31 (red) and cell nucleus (DAPI, blue) in xenograft tumor sections from the experiment performed in (B). (D) Diagram describes the experimental design of in vivo sunitinib-resistant (20mg/kg, daily) tumor generation followed with cabozantinib (40mg/kg, daily) treatment (10 mice per group). (E) The measurement of tumor size during the experiment of (D). The size difference between sunitinib and saline treated groups at same time point was analyzed using Student t-test. (* indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.01). (F) The mice were sacrificed after saline/sunitinib or cabozantinib treatment, the tumor tissue were obtained and equal amount of protein lysate were analyzed by western blot with specific antibodies as indicated. (G) Representative immunohistochemistry staining of CD31 (red) and cell nucleus (DAPI, blue) in xenograft tumor sections from the experiment performed in (F). (H) Proposed model for chronic sunitinib treatment-induced drug resistance.