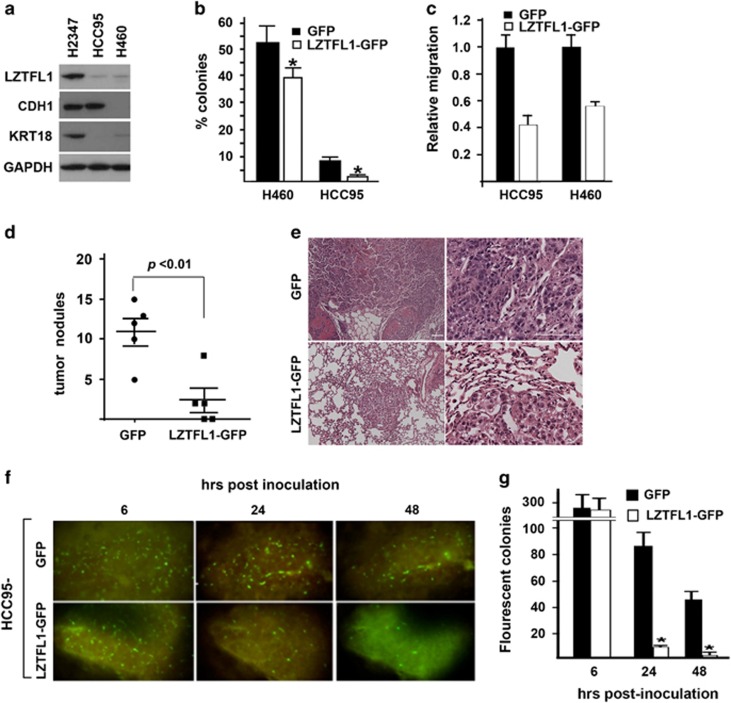
Figure 2.
LZTFL1 inhibits lung tumorigenesis. (a) Western blotting of LZTFL1 and epithelial markers (CDH1 and KRT18) in three lung cancer cell lines. LZTFL1 is expressed in H2347 cells and low (no) in HCC95 and H460 cells. (b) Colony-formation assays with GFP and LZTFL1-GFP expressing H460 and HCC95 cells grown in soft agar. Overexpression of LZTFL1 significantly inhibited colony-formation ability of the tumor cells (n=6±s.e.m.). (c) Relative migration ability of HCC95 and H460 cells transduced with either GFP or LZTFL1-GFP (n=4±s.e.m.). (d) H460-GFP or H460-LZTFL1-GFP cells were IV injected into NOD/SCID mice. Tumors were harvested 6 weeks later. The number of tumor nodules formed in the lung of mice injected with H460-LZTFL1-GFP cells were significantly lower than that of mice injected with control vector transfected cells (H460-GFP) (n=5±s.e.m.). (e) H&E staining of two representative lung sections from each experimental group in (d). (f) Control GFP or LZTFL1-GFP-expressing HCC95 cells were IV injected into a FVB mouse through the tail vein. Lungs were harvested within 15 min of tumor cell injection, sliced and cultured ex vivo. Representative serial images of fluorescent-labeled HCC95 cells in lung sections in the culture dish were taken at the indicated time points with Zeiss fluorescent microscope. (g) Fluorescent colonies were counted and averaged from 10 randomly chosen lung slices/experiment from three independent experiments (n=3±s.e.m.). *P<0.01.