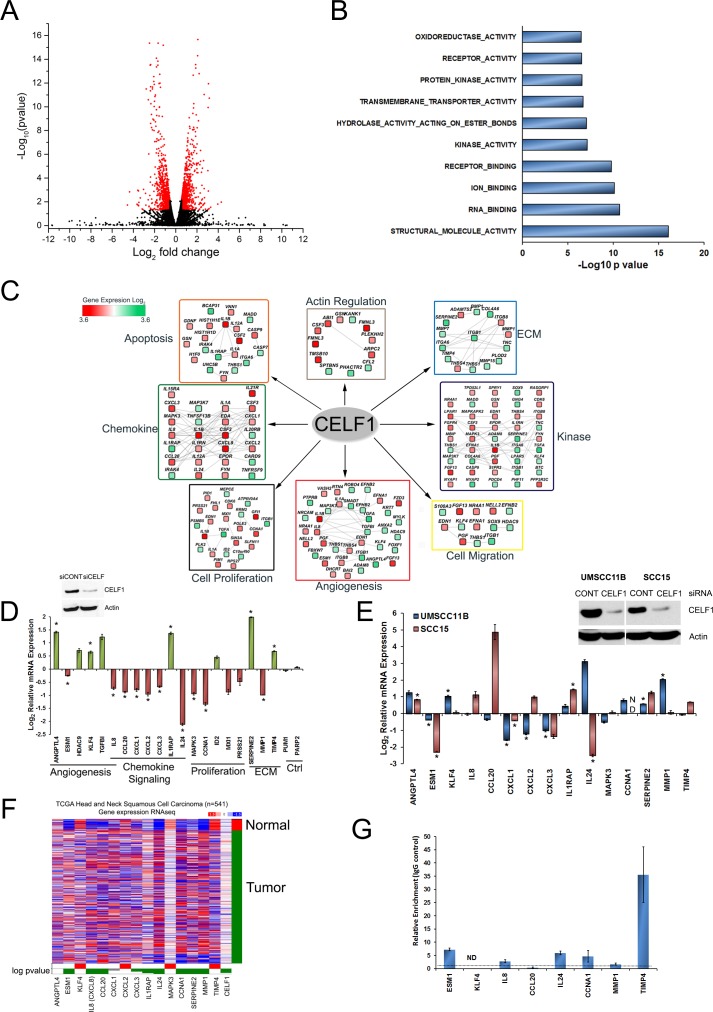
Figure 1. Next generation sequencing (RNA-seq) identifies novel targets regulated by CELF1.
A. Volcano plot of the 1283 significant differentially regulated mRNA transcripts (shown in red). B. GO (gene ontology) significantly enriched molecular function analysis of CELF1 controlled mRNAs. C. Biological process enrichment analysis of up (red) and down (green) CELF1 regulated transcripts. D. Validation of RNA-seq mRNA targets using qRT-PCR as a function of CELF1 expression. Down regulated transcripts (red); up regulated transcripts (green); neutral transcripts (gray). Bars represent mean ± SE; N = 3. *p value < 0.05. E. Validation of RNA-seq mRNA targets using qRT-PCR as a function of CELF1 expression in UMSCC-11B and SCC15 OSCC cell lines. Bars represent mean ± SE; N = 3. **p value < 0.05. F. Analysis of mRNA levels for the 15 validated mRNA targets using UCSC cancer genomics browser. TCGA HNSCC datasets were normalized and represented as a heatmap. Red: up regulated; blue: down regulated. Targets significantly upregulated in normal tissues (red); significantly upregulated in tumor tissues (green). Wilcoxon statistical analysis. G. Ribonucleoprotein immunoprecipitation (RNP-IP) of CELF1 associated mRNAs quantified using qRT-PCR. ND: Not detected in CELF1 immunolysates.