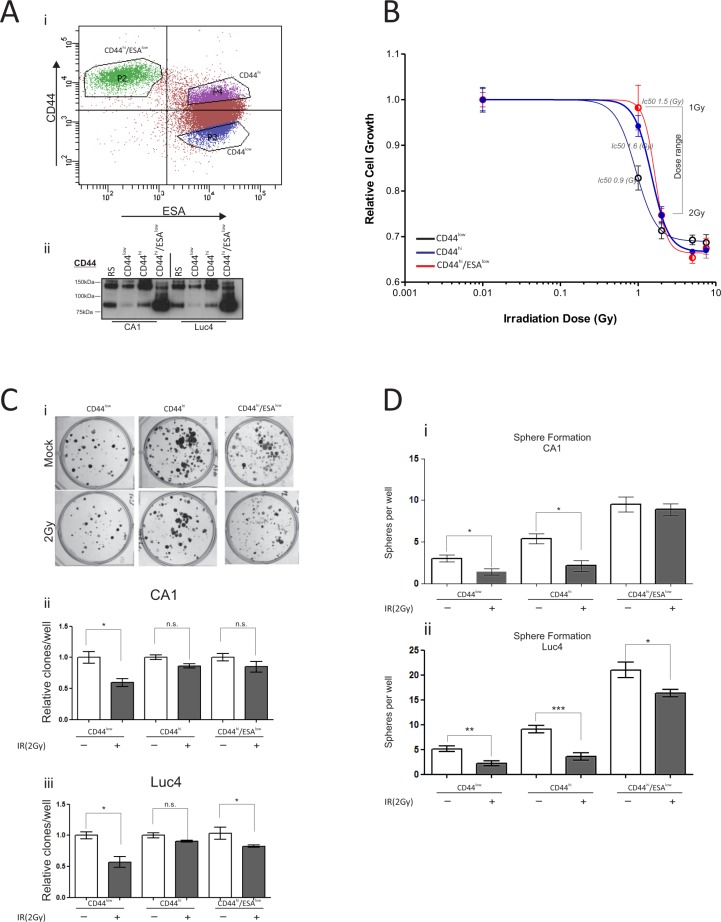
Figure 1. Oral CSC are more resistant to IR-induced growth arrest.
(Ai) Typical flow cytometry profile of CA1 cells stained with CD44-PE/ESA-APC. All three populations CD44low/ESAhi, CD44hi/ESAhi, and CD44hi/ESAlow were flow sorted and grown for five days. (Aii) Immuno-blot against anti-CD44, to verify population purity prior to irradiation treatment. (B) Epithelial stem cell populations are more resistant to radiation-induced growth arrest. All populations were treated individually, after flow sorting, with varying doses of γ-irradiation and proliferation was measured. CD44low/ESAhi was the most sensitive population to growth arrest (Ic50: 1Gy), when compared to the oral CSC populations (CD44hi/ESAlow Ic50: 1.5Gy; CD44hi/ESAhi Ic50: 1.6Gy). (Ci) Clonogenic assays were performed to measure the capacity of each population to form colonies after a 10-day period. There is a slightly reduced sensitivity of CSC in response to γ-irradiation, but the differences are not statistically significant (Cii, Ciii). (D) The sphere forming capacity of CD44hi/ESAlow cells (motile CSC) remained relatively stable following 2 Gy of IR. Both CD44hi/ESAhi and CD44low/ESAhi almost completely lost this ability following IR. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.