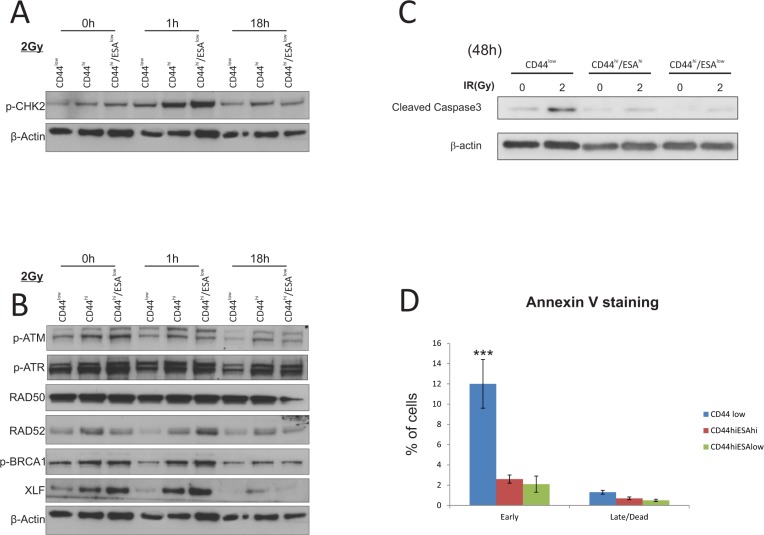
Figure 2. CSC show preferential activation of DNA damage and repair associated proteins.
Western Blot analysis of protein extracts from CA1 cells. All three populations were flow sorted, then allowed to grow for 5 days prior to a single exposure to 2Gy IR. Cells were allowed to recover prior to being lysed at 1 hour and 18 hours IR. (A) Total cell proteins were immuno-blotted against anti-pCHK2, γH2A.x, while β-actin was used as protein loading control. There is preferential activation of both proteins, specifically γH2A.x in CSC populations following IR treatment. (B) Total cell proteins were immuno-blotted against anti-pATM, anti-pATR, anti-RAD50, anti-RAD52, anti-pBRCA1, ant-XLF, while β-actin was used as protein loading control. Both types of CSC populations show preferential activation of RAD52, p-BRCA1, and XLF suggesting activation of the DNA repair pathway. (C) Immuno-blot against anti-cleaved Caspase3 following IR treatment with 2Gy. Longer time points revealed an apoptotic response for CA1 cells, with CSC populations showing a later response to IR treatment. Control CD44low/ESAhi cells show dramatic sensitisation to apoptosis starting 72 hours after 1Gy IR, while both CSC populations show a delayed response starting at 48 hours after 5Gy IR. β-actin was used as protein loading control. (D) AnnexinV/DAPI staining was performed on all separate fractions 2 days following treatment with 2Gy to detect live (AnnexinV(−)/DAPI(−)), early apoptotic (AnnexinV(+)/DAPI(−)), late apoptotic (AnnexinV(+)/DAPI(+)), and dead (AnnexinV(−)/DAPI(+)) cells. CD44low/ESAhi and CD44low/ESAlow populations show preferential resistance to early apoptosis when compared to CD44low/ESAlow control cells. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001