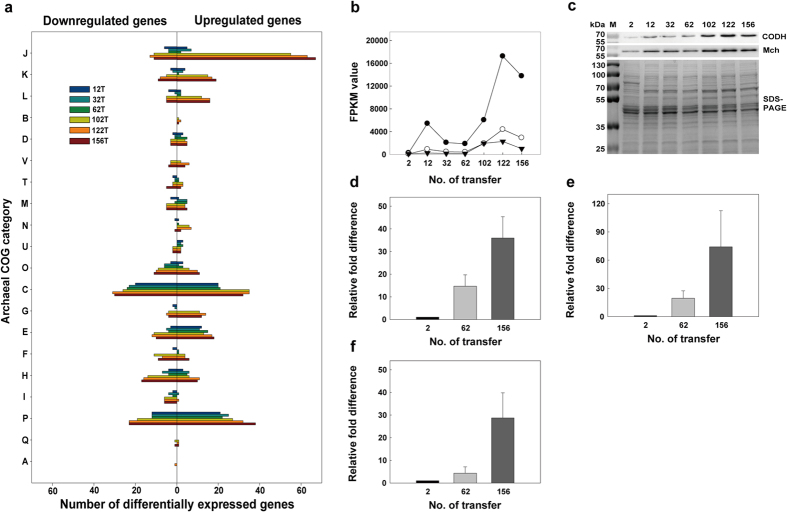
Figure 2. Archaeal COG classification of differentially expressed genes and changes in the expression levels of genes in the CODH gene cluster during adaptation.
(a) The following COG categories were included: J, Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis; K, Transcription; L, Replication, recombination and repair; B, Chromatin structure and dynamics; D, Cell cycle control, cell division and chromosome partitioning; V, Defense mechanisms; T, Signal transduction mechanisms; M, Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; N, Cell motility; U, Intracellular trafficking, secretion and vesicular transport; O, Posttranslational modification, protein turnover and chaperones; C, Energy production and conversion; G, Carbohydrate transport and metabolism; E, Amino acid transport and metabolism; F, Nucleotide transport and metabolism; H, Coenzyme transport and metabolism; I, Lipid transport and metabolism; P, Inorganic ion transport and metabolism; Q, Secondary metabolite biosynthesis, transport and catabolism; A, RNA processing and modification. The numbers of upregulated genes and downregulated genes are indicated as bars in the right and left panels of the histogram, respectively. (b) RNA-seq analysis of genes encoding CODH (TON_1018) (closed circle), Mch (TON_1023) (open circle) and Mnh (TON_1031) (closed inverted triangle). (c) Western blot analysis of TON_1018 (67.7 kDa) and TON_1023 (61.7 kDa). RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA abundance of TON_1018 (d), TON_1023 (e) and TON_1031 (f). Error bars indicate standard deviations from duplicate experiments. FPKM, Fragments per kilobase per million mapped reads; M, molecular mass marker.