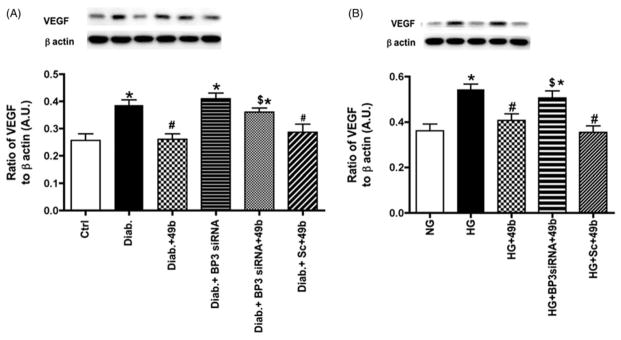
Figure 5.
Compound 49b significantly reduced VEGF in the diabetic rat retina and in REC cultured in high glucose. Figure A shows VEGF levels in control (Ctrl), diabetic (Diab), diabetic+Compound 49b (Diab+49b), diabetic+IGFBP-3 siRNA (Diab+Bp3 siRNA), diabetic+IGFBP-3 siRNA+Compound 49b (Diab+BP3 siRNA+49b) and diabetic+scrambled siRNA (Diab+scsiRNA) rat retina. Figure A demonstrates that Compound 49b significantly reduces VEGF levels through increasing IGFBP-3 levels. Figure B represent measurements of VEGF in REC cultured in normal (NG) or high glucose (HG) and high glucose and treated with Compound 49b (HG+49b), high glucose, IGFBP-3 siRNA and Compound 49b (HG+Bp3 siRNA+49b) and high glucose with scrambled siRNA+49b (HG+Sc+49b). High glucose conditions significantly increase VEGF levels, which are reduced by Compound 49b. *p<0.05 versus NG or control, #p<0.05 versus HG or diabetes, $p<0.05 versus HG+49b or Diab+49b. N=5–6 for rat retina and N=4 for cell work.