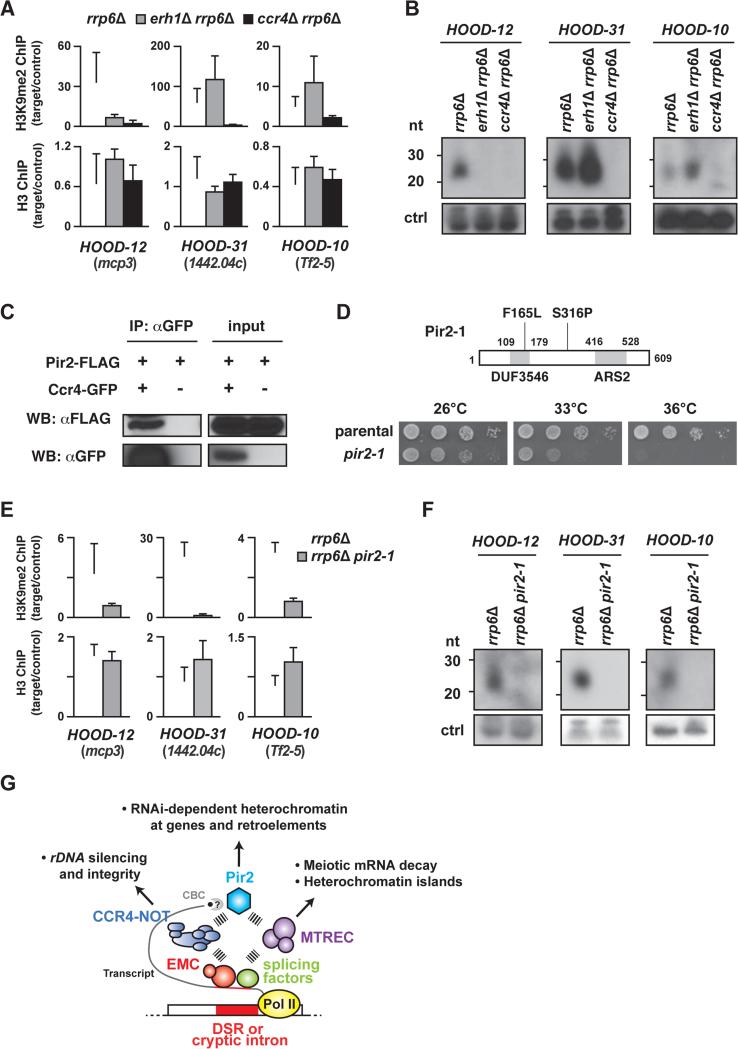
Figure 7. Ccr4 interacts with Pir2/ARS2 to promote small RNA production and H3K9 methylation at HOODs.
(A) ChIP-qPCR of H3K9me2 and H3 at Mmi1-dependent (HOOD-12) and Mmi1-independent HOODs (HOOD-31 and -10) in rrp6Δ (white bars), erh1Δ rrp6Δ (grey bars) and ccr4Δ rrp6Δ (black bars). The fold enrichment values of the target loci relative to the control locus vps33 are shown as the mean+SD (n=3). (B) Northern blot analysis of small RNA generation at three HOODs. Non-specific bands (~90 nt) served as a loading control (ctrl). (C) Co-immunoprecipitation of Pir2-FLAG with Ccr4-GFP. Cell lysates from the indicated strains were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-GFP antibody followed by Western blotting. (D) Schematic showing the pir2-1 allele, which encodes Pir2 protein containing Phe165 to Leu (F165L) and Ser316 to Pro (S316P) substitutions. Two conserved domains, DUF3546 and ARS2, are shown as grey boxes (top). Serial dilutions of parental wild-type (parental) and pir2-1 cultures were spotted onto rich plates and then incubated at the indicated temperatures (bottom). (E) ChIP-qPCR of H3K9me2 and H3 at Mmi1-dependent (HOOD-12) and Mmi1-independent HOODs (HOOD-31 and -10) in rrp6Δ (white bars) and rrp6Δ pir2-1 (grey bars). Fold enrichment of H3K9me2 and H3 at three target loci relative to the control locus (vps33) are shown as the mean+SD from three biological replicates. (F) Northern blot analysis of small RNAs generation at three HOODs. Non-specific bands (~90 nt) served as a loading control (ctrl). (G) Model showing EMC, CCR4-NOT, MTREC and Pir2 involvement in RNA-based regulation of gene expression and heterochromatin assembly. Transcripts containing a DSR are recognized by EMC, which in turn recruits MTREC and/or CCR4-NOT. MTREC is predominantly responsible for meiotic mRNA decay and formation of heterochromatin islands. On other hand, CCR4-NOT facilitates heterochromatin assembly at rDNA repeats and interacts with Pir2 (which also associates with Cap binding complex: CBC) and Pab2 (not depicted) to promote HOOD assembly at genes and retrotransposons. Pir2 is also known to associate with MTREC, implicated in formation of certain HOODs. In addition to the DSR, cryptic introns and splicing factors, which were previously implicated in the assembly of HOODs, likely also engage Pir2, CCR4-NOT and MTREC to promote mRNA decay and generate small RNAs mapping to HOODs. See also Figure S7.