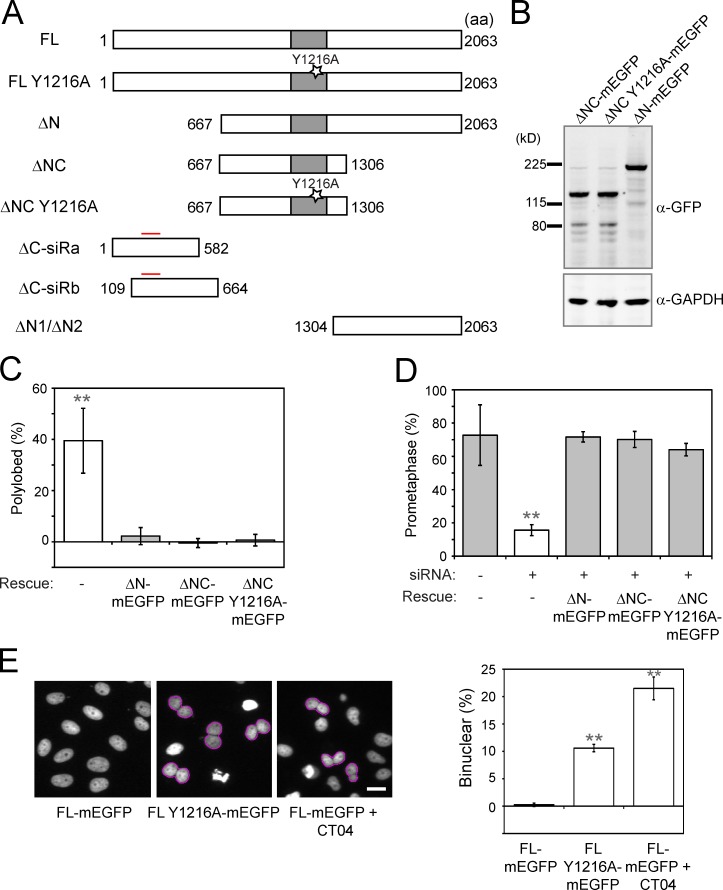
Figure 2.
ARHGEF17 fragment restores SAC function independently of catalytic activity for Rho GEF of ARHGEF17. (A) Schematic depiction of hARHGEF17 variants used in phenotypic rescue assays: FL: hARHGEF17 (1–2,063)-mEGFP; FL Y1216A: hARHGEF17 (1–2,063)-Y1216A-mEGFP; ΔN: hARHGEF17 (667–2,063)-mEGFP; ΔNC: hARHGEF17 (667–1,306)-mEGFP; ΔNC Y1216A: hARHGEF17 (667–1,306)-Y1216A-mEGFP; ΔC-siRa: hARHGEF17 (1–582)-mEGFP; ΔC-siRb: hARHGEF17 (109–664)-mEGFP; ΔN1: mEGFP-hARHGEF17 (1,304–2,063)-mEGFP; and ΔN2: hARHGEF17 (1,304–2,063)-mEGFP. Gray boxes indicate GEF activity domain (Dbl-homologous domain); Y1216A indicates the inactivating mutation in the GEF domain; red lines indicate sites for mutations for siRNA resistance. (B) Immunoblot analysis of hARHGEF17 fragments fused to GFP (detected with anti-GFP). GAPDH, loading control. (C and D) Rescue of hARHGEF17 knockdown-induced polylobulation (C) or SAC defect (D). Comparison of polylobed (C; normalized to Scrambled) or prometaphase population (D; nocodazole treated) rescued with hARHGEF17 fragments (ΔN-mEGFP, ΔNC-mEGFP, and ΔNC Y1216A-mEGFP) of >11,500 (C) or >6,300 (D) cells/three independent experiments. (E) Phenotypic analysis of cytokinesis defects (binucleation) of a catalytically inactive mutant of full-length ARHGEF17 (FL Y1216A) during mitosis. (left) H2B-mCherry, wild-type full-length (FL-mEGFP), catalytically inactive (FL Y1216A-mEGFP), or cells 24 h after CT04 treatment (0.25 mg/ml; FL + CT04). (right) Comparison of binuclear population of >3,000 cells/three independent experiments. Bar graphs show mean ± SD. **, P < 0.01 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test, compared with no rescue construct (C), si(Scrambled) without a rescue construct (D), or FL-mEGFP (E). Cells automatically segmented/analyzed by CellCognition. Bars, 10 µm.