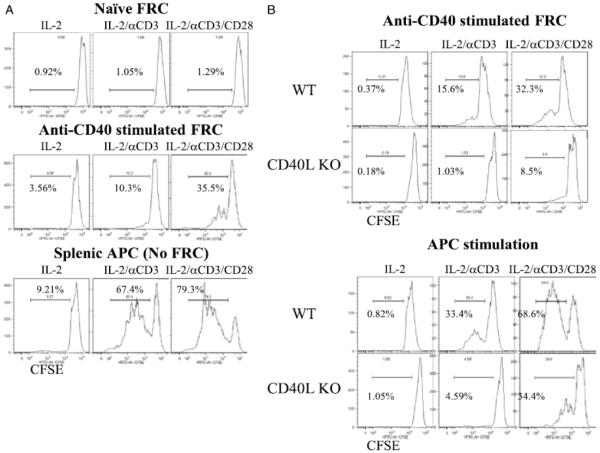
Figure 2. Activation status of FRC affects their ability to stimulate T cells.
(A.) Flow sorted naïve FRC (top), FRC activated by anti-CD40 mAb FGK4.5 for 12 hours and washed (middle), or CD4 depleted non-FRC APC (bottom) plus CFSE labeled CD4+ T cells added on the same day to cultures containing IL-2 (20 ng/ml), IL-2 + soluble anti-CD3 (0.3 μg/ml), or IL-2 + soluble anti-CD3 + anti-CD28 mAbs (0.3 μg/ml). (B.) Flow sorted FRC activated by anti-CD40 mAb FGK4.5 for 12 hours, FRC washed, and CFSE labeled WT or CD40L KO CD4+ T cells then added to culture (top). CFSE labeled WT or CD40L KO CD4+ T cells cultured with WT CD4-depleted, non-FRC, splenic APC (bottom). CD4+ T cells assayed 3 days later. Histograms gated on CD4+ T cells and the percent of proliferating cells shown. CD4 purity 90 to 97%. Representative of 3 independent experiments. FRC from 10 mice pooled for each experiment.