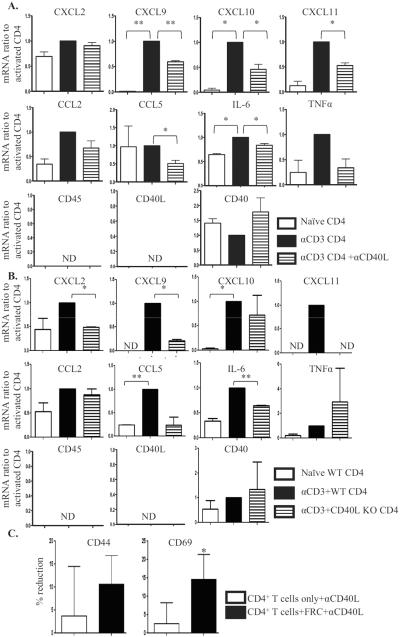
Figure 3. Activated CD4+ T cells stimulate FRC responses and FRC modulate T cell responses in a CD40L dependent manner.
CD4+ T cells unstimulated or stimulated in plates coated with 5μg/ml anti-CD3 mAb for 3 to 5 hours. Flow sorted FRC added to the CD4+ T cells for 18 hours, with or without anti-CD40L mAb (2 μg/ml). FRC and T cells re-sorted, and FRC mRNA isolated for qRT-PCR. (A.) mRNA expression in FRC activated by CD4+ T cells as a baseline (black), ratio of naïve FRC to baseline (white), and ratio of FRC activated by CD4+ T cells with anti-CD40L mAb to baseline (pattern). (B.) WT or CD40L KO CD4+ T cells unstimulated or stimulated in plates coated with 5 μg/ml anti-CD3 mAb for 3 to 5 hours. Flow sorted FRC added to the T cells for 18 hours. FRC and T cells re-sorted, and FRC mRNA isolated for qRT-PCR. mRNA expression in FRC activated by WT CD4+ T cells as baseline (black), ratio of naïve FRC to baseline (white), and ratio of FRC activated by CD40L KO CD4+ T cells to baseline (pattern). Results are from 3 independent experiments, each experiment from 10 mice pooled. ND: not detected. (C.) CD4+ T cells treated as above, CD4+ T cells only or CD4+ T cells with naïve FRC present were re-sorted for surface activation phenotype analysis by flow. Effect of anti-CD40L mAb was calculated as percent reduction of activation marker expression compared to population without anti-CD40L. Reduction by anti-CD40L in CD4+ T cells only (white) or in CD4+ T cells with FRC (black). Results from 4 independent experiments. Gated on CD4+ T cells. * p<0.05, ** p<0.005.