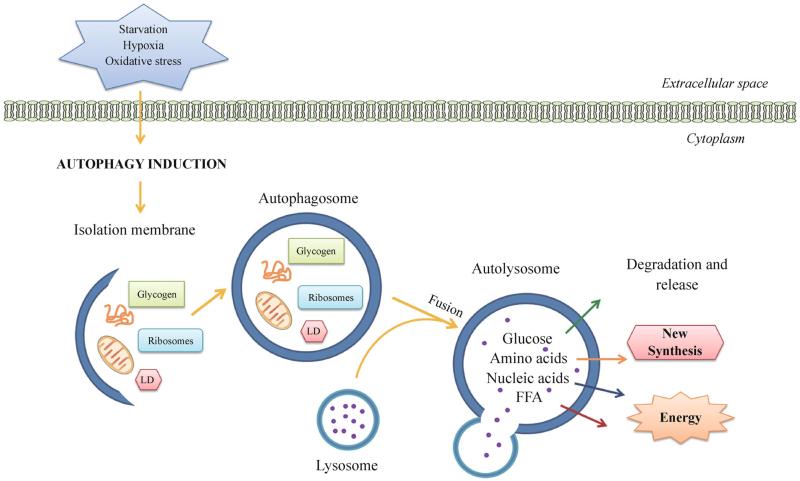
Figure 1.
Autophagy in organelle turnover and nutrient recycling. Autophagy is initiated by the formation of an isolation membrane (or phagophore) under stress conditions, such as nutrient deprivation, hypoxia and oxidative stress. The isolation membrane enwraps bulk cytosol or specific cargos (misfolded proteins, mitochondria, glycogen, ribosomes, lipid droplets, etc.), and elongates and forms a double-membrane autophagosome. It then fuses with the lysosome into an autolysosome, where the resident hydrolytic enzymes digest cargos and various resulting metabolites and macromolecules (including amino acids, glucose, nucleic acids and free fatty acids) are released back to the cytosol as new building blocks or energy sources. LD, lipid droplets; FFA, free fatty acids.