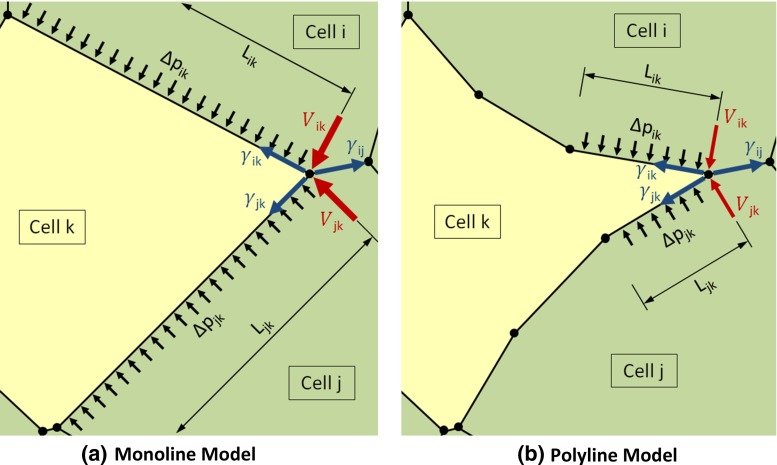
Fig. 2.
How monoline edges restrict motion. The edge tensions in the figure were chosen so that they should pull the yellow cell between the two green cells (Brodland 2002), though the lengths of the tension vectors do not reflect their relative magnitudes. However, when cell edges are forced to remain straight, as in (a), intracellular pressure differences can act over a long enough length that the equivalent shear forces they generate (Eq. 2) and transmit to the triple junction (in this case between cells i, j and k) can prematurely arrest its motion. When a polyline model is used (b), the segment lengths are shorter and the resulting shear forces have a much reduced effect