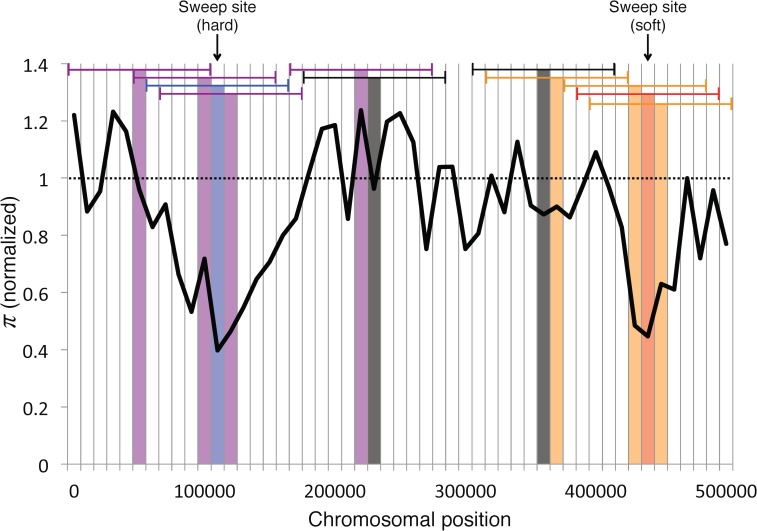
Fig 1. Examples of the five classes used by S/HIC.
S/HIC classifies each window as a hard sweep (blue), linked to a hard sweep (purple), a soft sweep (red), linked to a soft sweep (orange), or neutral (gray). This classifier accomplishes this by examining values of various summary statistics in 11 different windows in order to infer the mode of evolution in the central window (the horizontal blue, purple, red, orange, and gray brackets). Regions that are centered on a hard (soft) selective sweep are defined as hard (soft). Regions that are not centered on selective sweeps but have their diversity impacted by a hard (soft) selective sweep but are not centered on the sweep are defined as hard-linked (soft-linked). Remaining windows are defined as neutral. S/HIC is trained on simulated examples of these five classes in order to distinguish selective sweeps from linked and neutral regions in population genomic data.