Fig 5. Models derived from SEIRAS observations.
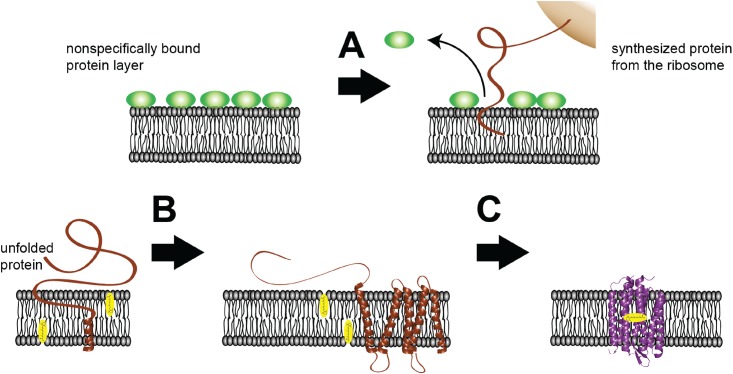
Before addition of the plasmid, the nanodisc monolayer is covered by nonspecifically bound protein (green spheres) of the E. coli cell extract. As DNA encoding bO is added, transcription and translation are initiated. Subsequently, the nascent polypeptide chain approaches the lipid bilayer surface (brown line). (A) Pre-adsorbed species are removed from the surface and the synthesized peptide inserts into the membrane. (B) During insertion, the peptide folds into individual transmembrane α-helices (brown helices). (C) Individual α-helices interact with each other, leading to folding of the final two helices G and F and formation of tertiary structure. Retinal (in yellow) at the lipid bilayer binds to the apo-protein and fully functional bR is formed. Tertiary structure formation is enhanced when retinal is pre-bound to the lipid bilayer.