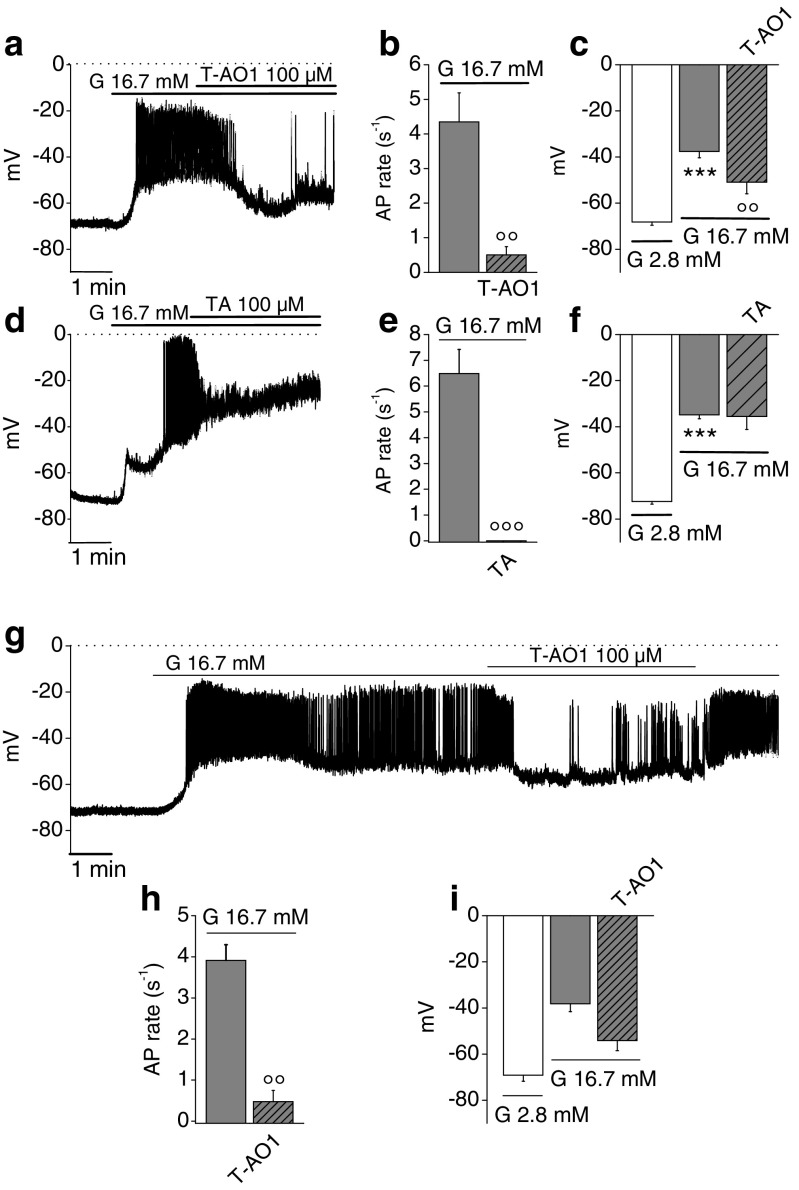
Fig. 4.
Effect of Ano1 inhibitors on the membrane potential of 16.7 mM glucose-stimulated murine dispersed β-cells. Zero-current nystatin-perforated patch-clamp voltage recordings performed on dispersed β-cells stimulated with 16.7 mM glucose before incubation with T-AO1 or TA (100 μM) in the bathing medium. Sampling rate, 18 kHz; 2-kHz filter setting. Dotted lines represent zero-voltage level. a–f Experiments carried out on rat dispersed β-cells, n = 7 from three preparations of rat dispersed islet cells in presence of T-AO1 and n = 8 from two preparations of rat dispersed islet cells with TA. a Representative recording ± T-AO1. Effect of T-AO1 b on AP rate and c on average membrane potential. d Representative recording ± TA. Effect of TA e on AP rate and f on average membrane potential. g–i Experiments carried out on mice dispersed β-cells, n = 4 from one preparation of mice dispersed islet cells. g Representative recording ± T-AO1. Effect of T-AO1 h on AP rate and i on average membrane potential. Repeated measures ANOVA test on c, P = 0.00123; f, P = 2 × 10−4; Friedman test on i, P = 0.18. ***P < 0.001 vs. 2.8 mM glucose condition; °°P < 0.01, °°°P < 0.001 vs. 16.7 mM glucose condition (least significant difference tests in c, f; paired Student’s t tests in b, e, h)