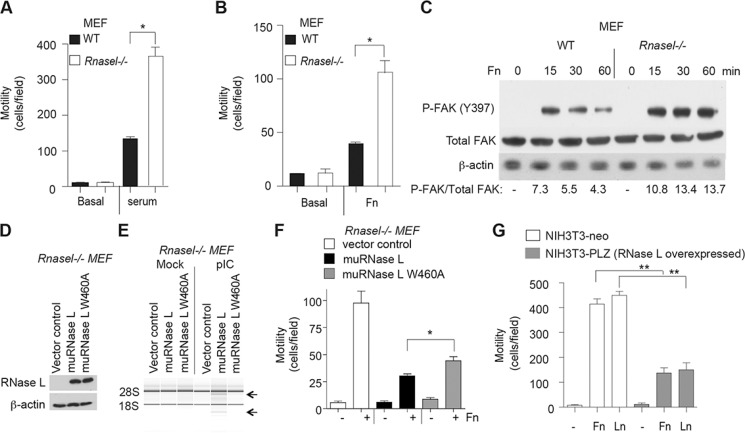
Figure 4. Suppression of mouse fibroblast migration by RNase L.
(A, B) Transwell assays showing migration of WT MEF and Rnasel−/− MEF in response to (A) serum or (B) fibronectin (FN). (C) Levels of FAK phosphorylated on tyrosine 397, total FAK, and β-actin levels from WT MEF and Rnasel−/− MEF after plating on dishes coated with FN for different times (as indicated) determined by immunoblotting. (D) Expression of flag-tagged mouse WT RNase L cDNA and mouse mutant RNase L W630A cDNA in Rnasel−/− MEF as determined by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG antibody. (E) RNA integrity before and after pIC transfection as determined in an RNA chip (Agilent). (F) Cell migration in transwell assays in response to fibronectin (Fn). (G) Migration of NIH3T3-neo and NIH3T3-PLZ cells over-expressing human RNase L in the presence of FN or laminin (LN). A,B,F,G. Data are shown as the mean ± SD each from a single experiment with 3 technical replicates. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001by Student's two-tailed t tests. The experiments were conducted 3 times (biological replicates) with similar results.