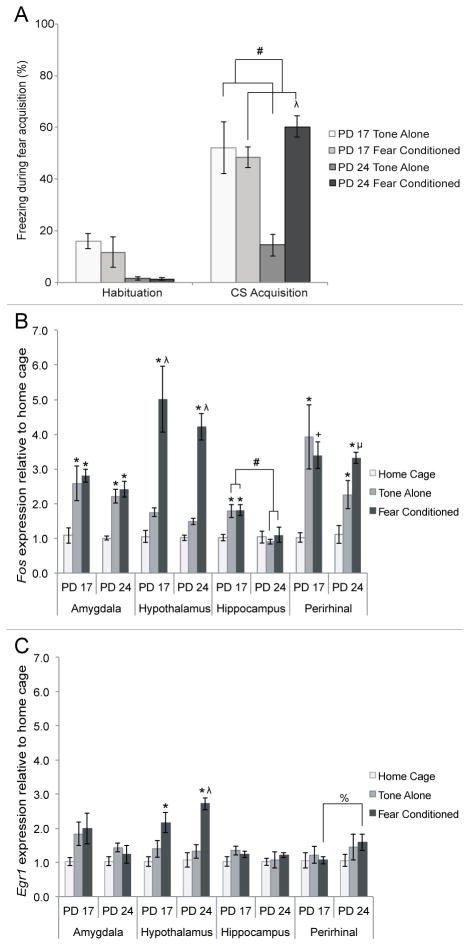
Figure 7. Behavioral and IEG mRNA concentration at PD 17 or PD 24 following fear conditioning (fear conditioned), exposure to tone alone (tone-alone) or no conditioning (home cage).
A) Amount of freezing behavior measured during habituation and while subjects were exposed to the tone during fear acquisition. Older, not younger, subjects exposed to both the tone and shock exhibited higher amounts of freezing compared to those exposed to just the tone. Additionally, tone-alone subjects were found to freeze less than fear conditioned ones. B) Fos mRNA levels in the amygdala, hypothalamus, hippocampus and perirhinal cortex following fear acquisition. One-way ANOVAs for age and condition showed significant differences due to condition in all four regions, and a significant difference due to age in the hippocampus. C) Egr1 levels in the amygdala, hypothalamus, hippocampus and perirhinal cortex following fear acquisition. One-way ANOVAs for age and condition revealed a significant difference due to condition in the hypothalamus of fear conditioned subjects only. Different from home cage: * = p<.05, + = p<.10; Different from tone-alone: λ = p<.05, μ = p<.10; All other differences: # = p<.05, % = p<.10