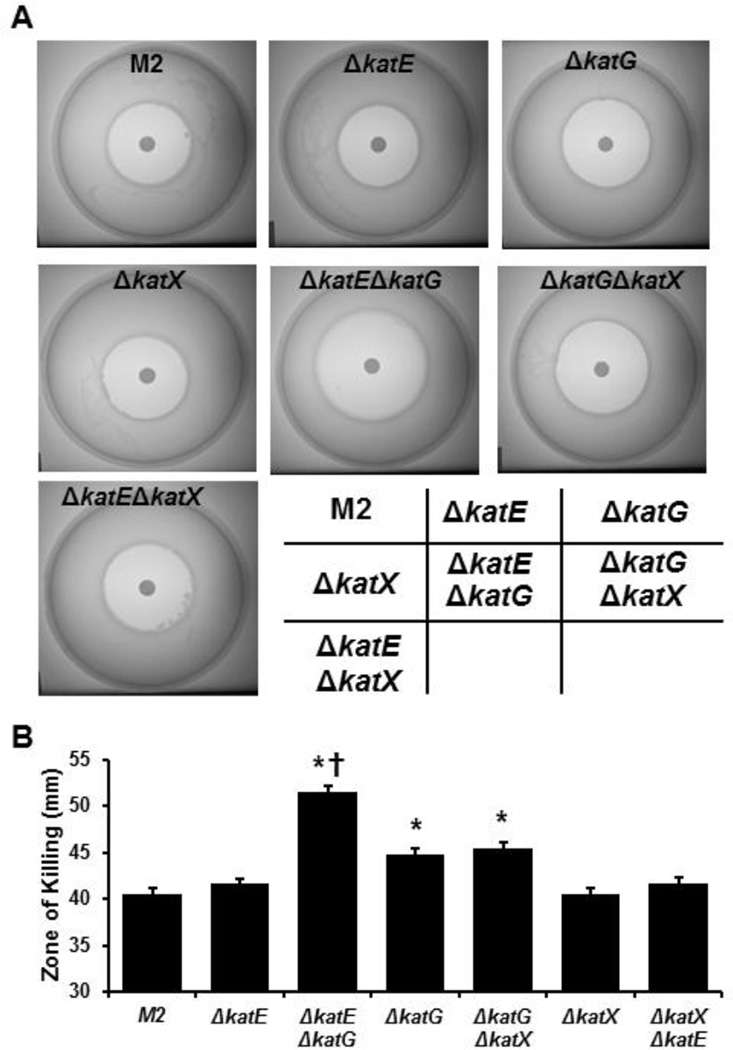
Figure 4.
The sensitivity of WT M2 A. nosocomialis strain and its derivatives deficient in katE, katG, both katE and katG to H2O2. The A. nosocomialis strains were cultured overnight, and then grown for 5 hours in fresh medium. Bacteria were adjusted according to their optical densities and seeded into soft agar on tryptic soy broth medium containing 1.5% agar. Hydrogen peroxide (2%, 10 µl) was spotted onto sterilized dry filter discs of 8-mm diameter. The plates were incubated at 37°C overnight. The halos were photographed and diameters of the halos were measured using a digital caliper. A. Halo formation caused by H2O2 on lawn containing different A. nosocomialis strains. Representative images are shown. B. Diameters of the halos caused by H2O2 for distinct A. nosocomialis strains. Bars are means ± standard error from 5 independent experiments. *, p<0.05, compared to the parental M2 strain. †, p<0.05, compared to the ΔkatG strain. Student’s t-test was used for comparison.