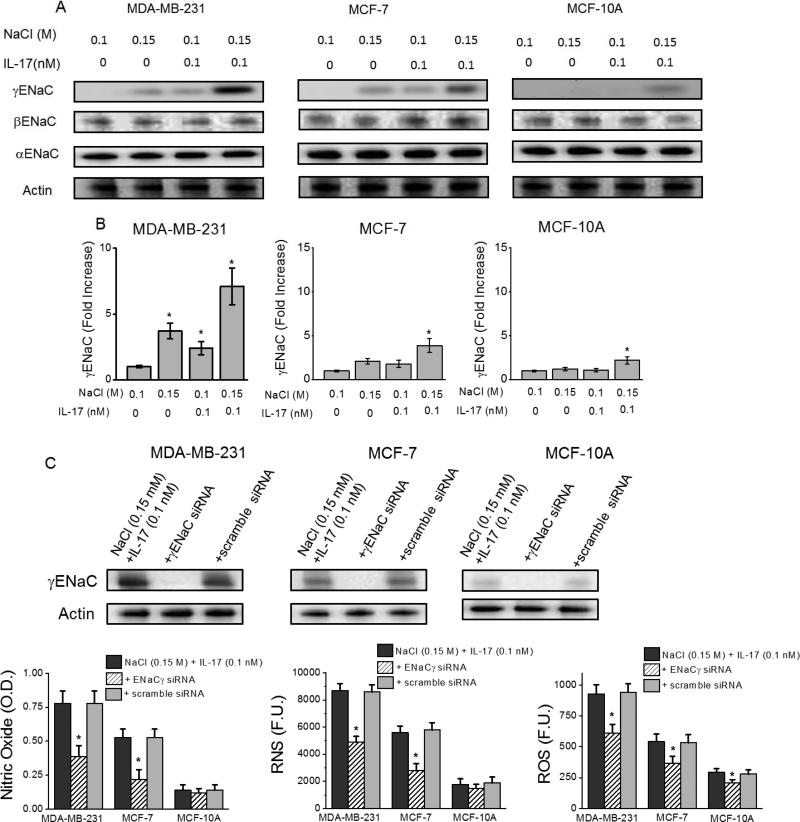
Figure 3.
γENaC mediates high sodium chloride induced inflammatory stress. (A) Western blot analysis of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) isoforms (-α, -β, -γ) following treatment with NaCl (0.15 M) and/or IL-17 (0.1 nM in basal 0.1 M NaCl media) in three cell lines; (B) mRNA analysis for γENaC expression in various breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231, MCF-7 and MCF-10a) following co-treatment with high salt (0.15 M M NaCl) and 0.1 nM IL-17. (C) Efficient knock-down of γENaC by specific siRNA, while scramble siRNA does not decrease expression of γENaC. (D-F) Inhibition of nitric oxide (C), RNS (D) and ROS (E) release following siRNA knock-down of γENaC. Data represented mean values ± SEM from five independent experiments. Student-t-test performed for statistical analysis (significance p<0.05).