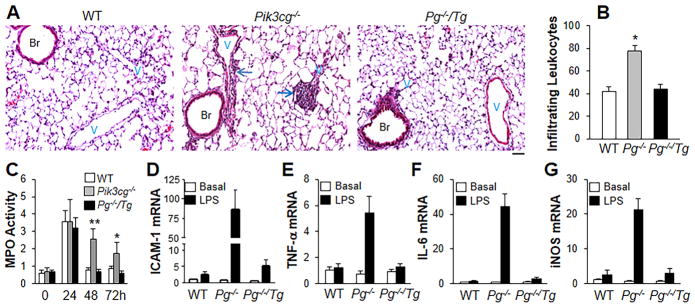
Figure 3.
Restoration of FoxM1 expression in Pg−/−/Tg mice mitigates lung inflammation. (A) H & E staining of lung sections (of 3 independent experiments) showing perivascular leukocyte infiltration in Pik3cg−/− mouse lungs at 48h post-LPS challenge. Arrows indicate leukocyte infiltration. Scale bar, 50 μm. Br, bronchia; V, vessel. (B) Analysis of infiltrating leukocytes in lungs at 48h post-LPS challenge. Bar graphs show infiltrating leukocytes per vessels (> 30μm in diameter). n = 5. *, P < 0.05(ANOVA). P−/−, Pik3cg−/−. (C) Time course of MPO activity in mouse lungs following LPS challenge (7.5 mg/kg, i.p.). n =5. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001 (ANOVA). (D–G) QRT-PCR analysis of expression of proinflammatory mediators in mouse lungs. AT 48h post-LPS challenge, mouse lungs were collected for QRT-PCR analysis. n = 5. Elevated expression of pro-inflammatory mediators seen in Pik3cg−/− mouse lungs was inhibited in Pg−/−/Tg mouse lungs.