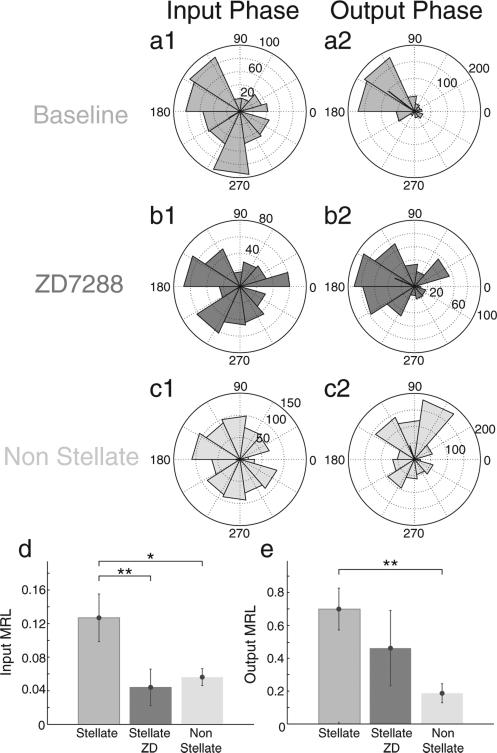
Fig. 6.
Ih is necessary for phase specificity of hyperpolarization induced rebound spiking. (a–c) Rose plots for standard inputs in stellate cells (n = 6) before (a) and after (b) application of ZD7288 as well as in non-stellate cells (n = 7, c). Rose plots display phase histograms for hyperpolarizing input pulses that induce spiking (a1, b1, c1) and for output spiking phase (a2, b2, c2). (d) Summary bar graph demonstrates that following h-current blockade, stellate cells lose the phase specificity for hyperpolarizing input, as indicated by a significant decrease in hyperpolarizing input MRL (paired t-test, **p < 0.01). Furthermore, this significant lack of input specificity is also present in non-stellate cells compared to baseline stellate cells (paired t-test, *p < 0.05). (e) Summary bar graph demonstrates that blocking the h-current in stellate cells decreases the specificity of output spiking phase, shown by a decrease in the MRL of output spiking phase, but this does not reach statistical significance. However compared to stellate cells, non-stellate cells display a significantly smaller MRL (paired t-test, **p < 0.01), and therefore, less phase specificity of output spiking.