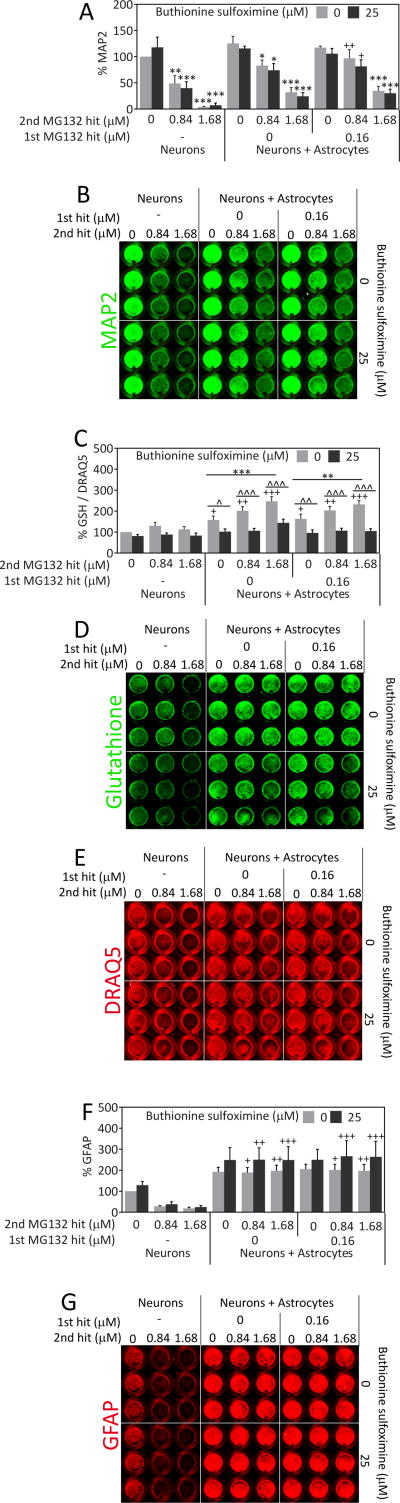
Fig. 6.
Severely stressed astrocytes can protect neurons from proteotoxic stress. A) Astrocytes were treated with the 1st MG132 hit or vehicle 24h prior to introduction of neocortical neurons, in the absence or presence of the glutathione synthesis inhibitor buthionine sulfoximine (BSO). Two days after the introduction of neurons, the neuron/astrocyte co-cultures were treated with MG132 as a 2nd hit or vehicle in the absence or presence of BSO. Two days after the 2nd hit, neuronal viability was measured by the In-Cell Western assay for the specific neuronal marker MAP2. B) Representative image of MAP2 In-Cell Western. C) Changes in glutathione levels were measured by In-Cell Western analyses and expressed as a function of the infrared nuclear stain DRAQ5 to control for changes in cell density. Representative images of glutathione immunostaining (D) and DRAQ5 levels (E) are included. F) The astrocytic marker GFAP was measured by In-Cell Western analysis in neuron/astrocyte co-cultures 48h after the 2nd MG132 hit or vehicle treatment in the absence or presence of BSO. G) Representative image of GFAP In-Cell Western. ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001 vs 0 μM 2nd MG132 hit; + p ≤ 0.05, ++ p ≤ 0.01, +++ p ≤ 0.001 vs neurons; ^ p ≤ 0.05, ^^ p ≤ 0.01, ^^^ p ≤ 0.001 vs 0 μM BSO, three-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc correction