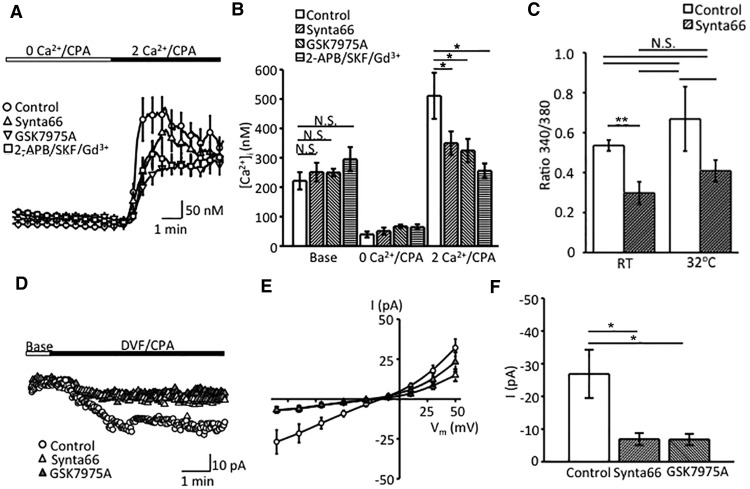
Figure 5.
Orai channels contribute to Müller glial SOCE. A, Comparison of store depletion-evoked [Ca2+]i responses in the presence of Orai and SOC inhibitors. The Orai inhibitor Synta66 (10 μm; blue trace) partially inhibits the peak and plateau overshoot response. Additional reduction is observed in the presence of the SOC inhibitor cocktail (red trace). B, Summary graph for the calibrated [Ca2+]i response during Orai and SOC channel blockade. Data are reported as the mean ± SEM. N.S., nonsignificant. *p < 0.05. C, Increase in temperature from RT to 32°C slightly increases the amplitude of SOCE responses (white bars) without changing the relative contribution of Orai channels (dappled bars denote responses in the presence of Synta66). D, Representative inward currents, induced by CPA in DVF saline. Synta66 and GSK-7975A partially inhibit the depletion-induced inward current. E, Averaged I–V curves of depletion-evoked transmembrane currents in untreated controls (n = 10, N = 3), Synta66-treated cells (n = 10, N = 3; blue trace), and GSK7975A-treated cells (n = 10, N = 2; orange trace). F, Summary graphs for depletion evoked current responses in the presence of Orai antagonists. Shown are mean ± SEM values of the amplitude of current at 100 mV. *p < 0.0.