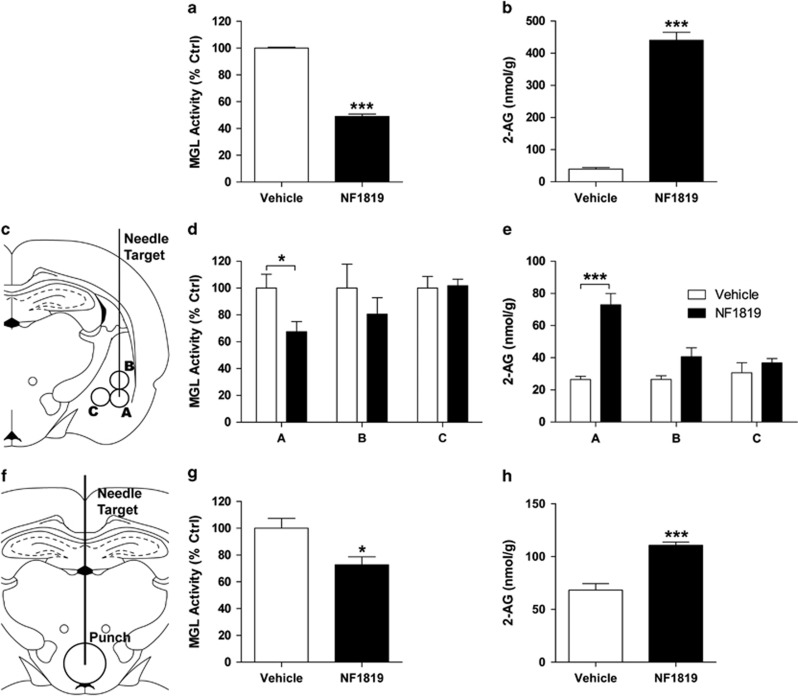
Figure 4.
Effects of NF1819 on MGL activity and 2-AG mobilization. (a) Intraperitoneal injection of NF1819 (5 mg/kg) lowers rat MGL activity and (b) increases 2-AG content in mouse brain. (c–e) Infusion of NF1819 into the BLA inhibits local MGL activity and increases 2-AG level. (c) Diagram of the needle tract and location of brain punches taken to measure MGL activity and 2-AG levels in the amygdala. (d) NF1819 infusion into the BLA inhibits MGL activity and (e) increases 2-AG levels at the site of injection (A) but not in nearby tissue (B–C; n=4 rats per group). (f–h) Infusion of NF1819 into the third ventricle inhibits MGL activity and increases 2-AG level in the hypothalamus. (f) Diagram of the needle tract and location of brain punches taken to measure MGL activity and 2-AG levels in the hypothalamus. (g) NF1819 infusion into the third ventricle inhibits MGL activity and (h) increases 2-AG levels in the hypothalamus (n=4 rats per group). Results are expressed as mean ±SEM; *P<0.05, ***P<0.001. BLA, basolateral amygdala; MGL, monoacylglycerol lipase.