Figure 2.
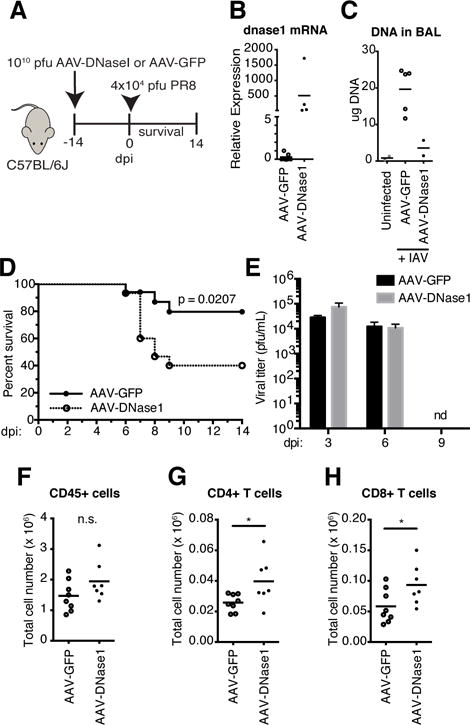
DNA in the lung is protective to IAV infection.
(A) Schematic for transduced expression of DNaseI. (B) dnase1 mRNA measured by qPCR with total RNA isolated from lungs of AAV-GFP and AAV-DNaseI treated mice. (C) DNA in cell-depleted BAL fluid in uninfected controls compared to AAV-GFP and AAV-DNaseI treated mice at 5 dpi with PR8. (D) Survival comparison between AAV-GFP and AAV-DNaseI treated WT mice challenged with 4 ×104 pfu PR8. Data combined from two independent experiments (AAV-GFP, n = 17; AAV-DNaseI, n = 15). (E) Viral titers of lung homogenates from AAV-GFP and AAV-DNaseI treated mice at 3, 6, and 9 dpi with PR8. (F–H)) Total number of CD45+ leukocytes (F), CD4+ T cells (G), and CD8+ T cells (H) in the total lungs of AAV-GFP and AAV-DNaseI treated mice at 5 dpi with PR8. *, P 0.05
