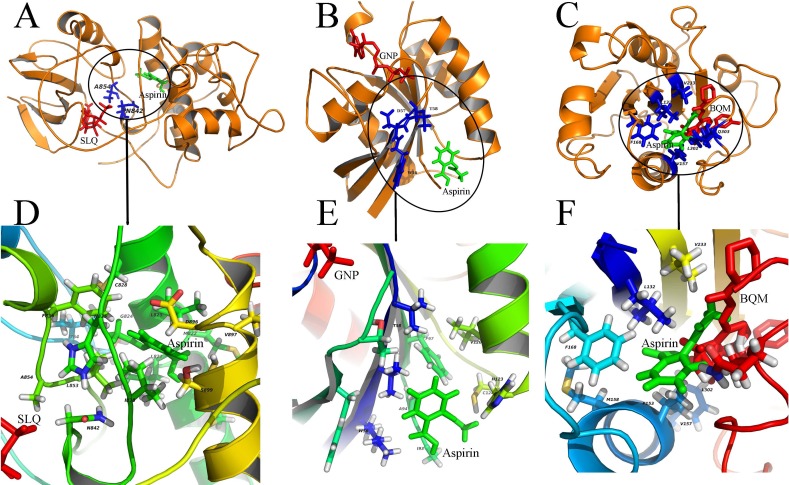
Figure 3. Diverse binding modes of aspirin to the putative targets.
The docking experiments reveal diverse binding modes of aspirin to these targets (A) Aspirin binding to protein CDK13 (3LQ5.pdb). (B) Aspirin binding to protein RAC1 (1RYH.pdb). © Aspirin binding to protein ITGAL (3BQM.pdb). The overview and close-up view of the binding mode of aspirin to their putative targets are shown in A-C and D-F, respectively. The close-up view (D-F) show all amino acids in the vicinity of aspirin. Aspirin and the known ligands of the three proteins are colored with green and red, respectively (A-C). The residues involved in binding to both aspirin and the ligands are shown as sticks and colored with blue (A-C). SLQ (A), GNP (B) and BQM © are ATP-analog inhibitor of the kinase CDK13, the substrate of the protein RAC1 and the inhibitor of protein ITGAL, respectively.