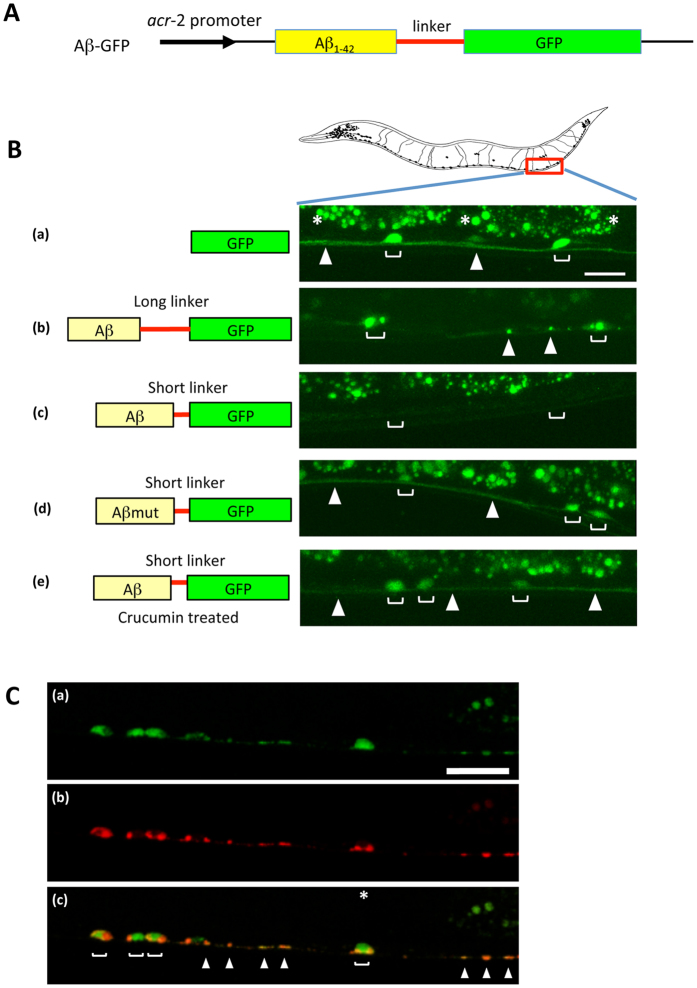
Figure 5. Expression of Aβ-GFP fusion proteins in C. elegans.
(A) Schematic representation of the Aβ-GFP fusion construct. (B) GFP fluorescence in the cholinergic motor neurons of Aβ-GFP transgenic C. elegans. The left illustration depicts the expressed proteins shown in the right pictures. The right pictures show the expression patterns of fusion proteins in C. elegans. (a) GFP, (b) Aβ-GFP with a long-linker, (c) Aβ-GFP with a short-linker, (d) Aβmut-GFP with a short-linker, and (e) crucumin treatment of animals bearing a short linker protein. Blankets indicate the cell bodies of neurons and arrowheads indicate the axon in the ventral nerve cord. Asterisks indicate the autofluorescence from the intestine. The long-linker has 14 amino acids and the short-linker has only 2 amino acids sequences. Cells expressing the short-linker Aβ-GFP protein did not show fluorescence (c) but the long-linker one and Aβmut-GFP showed bright fluorescence (b,d). Short-linker Aβ-GFP transgenic C. elegans were treated with curcumin, which induces Aβ disaggregation. Disappeared fluorescence was recovered after treatment with curcumin (e). Scale bar: 10 μm. (C) Localization of the Aβ-GFP fusion protein at the presynaptic regions. Aβ-GFP (a) and presynaptic protein SNB-1 fused with mCherry (b) were simultaneously expressed in cholinergic neurons. Several GFP puncta were co-localized with SNB-1 on the axon (c) suggesting that the fusion protein may be strongly accumulated at synaptic sites. Scale bar: 10 μm.