Fig. 1.
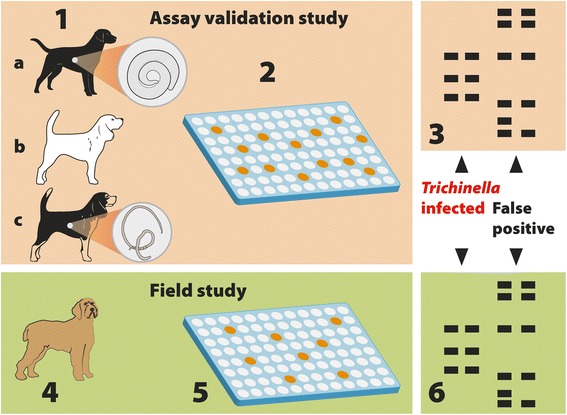
Study design. Assay validation study: 1. Serum samples were collected from Trichinella spp.-infected dogs and foxes (n = 21) (a), Trichinella-free dogs (n = 523) (b), and from Trichinella-free dogs (n = 75), which were infected with ancylostomatid nematodes, and/or Diphylidium caninum, and/or Toxocara canis, or Dirofilaria immitis (c). 2. Serum samples were tested by ELISA using excretory/secretory Trichinella spiralis muscle larva antigens (T_ESA). 3. ELISA-positive sera were tested by Western blot using T_ESA. Field study: 4. Serum samples were collected from wild boar hunting dogs (n = 384). 5. Sera were tested by the validated ELISA. 6. ELISA-positive sera were tested by the validated Western blot using T_ESA to distinguish sera of Trichinella-infected dogs from sera of false-positive dogs
