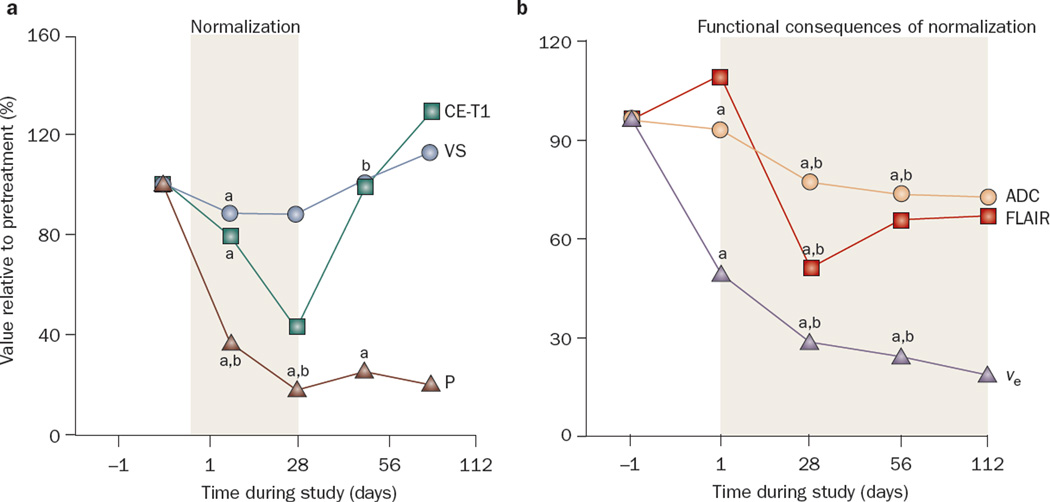
Figure 3.
Effects of cediranib on cerebral edema in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. a | Median values for contrast-enhanced T1-weighted tumor volume (CE-T1), vessel size (VS), and permeability (P) of the tumor over time as measured by an independent expert. Day –1 was set as 100% in all tumors, and changes during cediranib treatment were plotted for all patients. Note the rebound of CE-T1 volume and vessel size after day 28, which indicates a partial closure of the normalization window. By contrast, permeability (P) remains diminished for a longer period of time. b | Median values of potential MRI markers of cerebral edema including T2-weighted abnormality volume measured by fluid attenuated inversion recovery images (FLAIR), apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), and extracellular–extravascular volume fraction (ve), before and during treatment, showing a sustained decrease of edema while taking cediranib. aP <0.05 for values compared with day –1. bP <0.05 for values compared with day +1. Abbreviations: ADC, apparent diffusion coefficient; CE-T1, contrast-enhanced T1-weighted tumor volume; FLAIR, fluid attenuation inversion recovery; P, permeability; ve, extracellular–extravascular volume fraction; VS, vessel size. Permission obtained from Elsevier © Batchelor, T. T. et al. AZD2171, a pan-VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, normalizes tumor vasculature and alleviates edema in glioblastoma patients. Cancer Cell 11, 83–95 (2007).