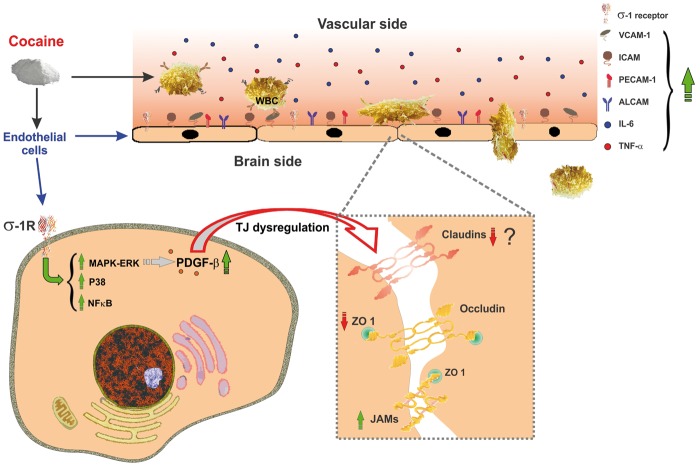
Figure 3.
Cocaine induces BBB dysfunction. Cocaine interacts with σ1 receptors on the BBB endothelium and elicits activation of p38 MAPK signaling pathways and NF-κB nuclear translocation. Downstream to the activation of p38 MAPK, cocaine up-regulates the expression of PDGF-β. This leads to compromised TJ integrity through down-regulation of ZO-1 and claudin-5. Additionally, cocaine promotes the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g. IL-6, TNF-α) from circulating WBCs and expression of BBB endothelial adhesion molecules that facilitate endothelial-leukocyte interaction and infiltration into the brain parenchyma.
BBB: blood-brain barrier; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; PDGF-β: platelet-derived growth factor-beta; TJ: tight junctional; ZO-1: zonula occludentes-1; IL: interleukin; TNFα: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; WBC: white blood cell.