Fig 1. Generation and validation of Foxn1G reporter mice.
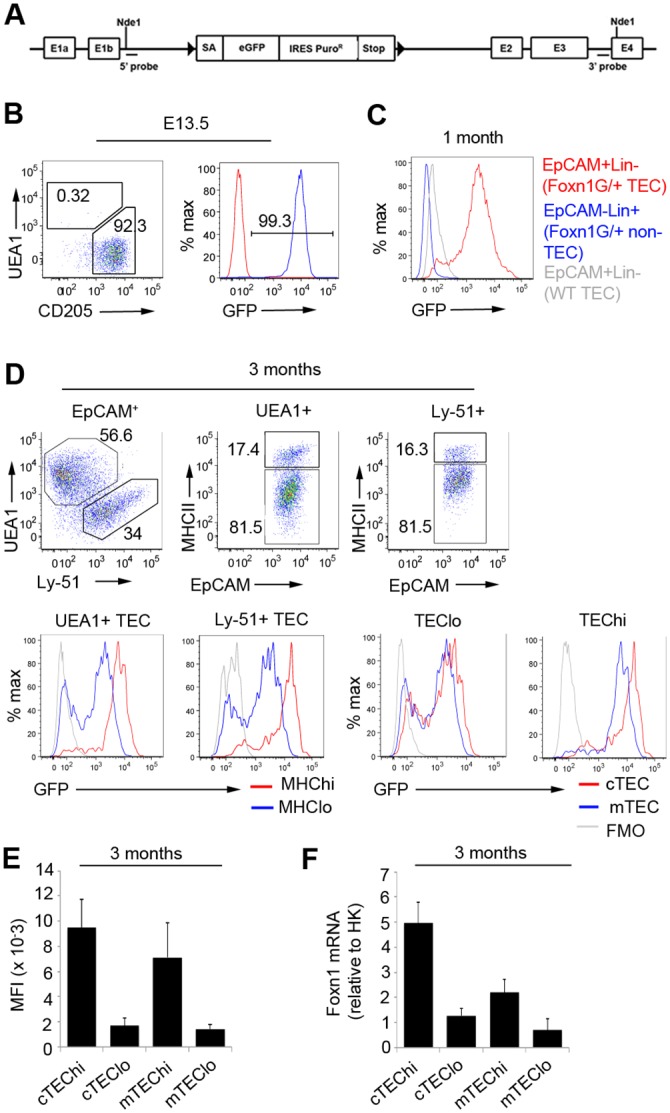
(A) Schematic representation of the Foxn1G allele. A LoxP flanked cassette containing the 5’ engrailed 2 splice acceptor site (SA), eGFP, an internal ribosome entry site coupled to the puromycin resistance fusion protein (IRES-PuroR), and the CMAZ transcriptional pause (Stop) [19] was inserted into intron 1b of the Foxn1 locus of mouse ES cells. E, exon. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of E13.5 Foxn1G/+ thymic primordia. Plots show data after gating against Lineage+ cells (Lin) and on total EpCAM+ cells. Left plot shows analysis with UEA1 and anti-CD205. WT, wild type. Red line shows FMO. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of thymi from 1 month old Foxn1G/+ or WT mice. Plots display data from total EpCAM+Lin- or EpCAM-Lin+, as shown. Absolute number of EpCAM+ cells for 1 month old Foxn1G/+ mice, 6.06x104±2.10 x 104. (D) Flow cytometric analysis of 3 month old Foxn1G/+ thymi after staining with the markers shown. Plots show subpopulations of EpCAM+ cells, as shown. Absolute number of EpCAM+ cells for 3 month old Foxn1G/+ mice, 5.41x104±6.97x103. (E) Median fluorescence intensities (MFI) for data shown in (D). (F) RT-qPCR analysis showing relative Foxn1 mRNA expression level in the populations shown, after purification by flow cytometry. (B) n = 4, (C) n = 5, (D,E) n = 6, (F) n = 5 independent biological experiments.
