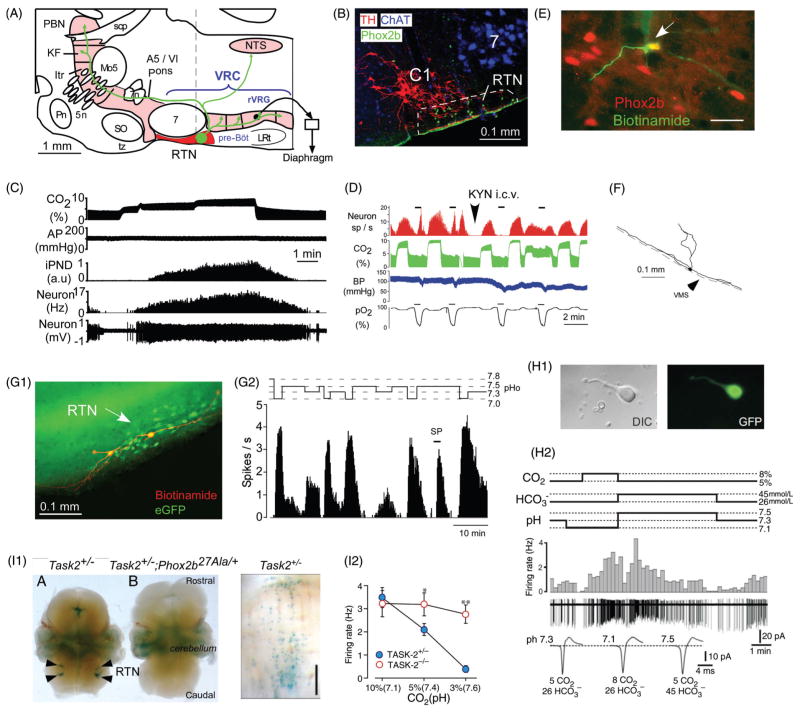
Figure 5.
Activation of RTN neurons by CO2. (A) Location and anatomical projections of RTN neurons (definition of RTN in Fig. 2 legend; abbreviations as in Fig. 2). (B) Transverse section through the lower right quadrant of the rat medulla oblongata at the level of the dotted line in A. The facial motor nucleus is in blue (choline acetyl-transferase immunoreactivity), the C1 presympathetic neurons are in red (tyrosine hydroxylase) and phox2b immunoreactivity (green, nuclear localization) identifies RTN neurons [adapted, with permission, from (401)]. (C) Response of an RTN neuron to graded hypercapnia in an anesthetized rat (end-expiratory CO2 shown in top trace) [adapted, with permission, from (401)]. (D) Example of one RTN neuron excited by brief hypoxia (carotid body stimulation, bottom trace) and by hypercapnia (end-expiratory CO2 in green). After i.c.v. administration of the broad spectrum glutamatergic blocker kynurenic acid, the cell no longer responds to hypoxia but its response to hypercapnia is unaffected [adapted, with permission, from (300)]. (E) RTN CO2-activated neuron labeled juxtacellularly with biotinamide in vivo (green fluorescence) has a Phox2b-ir nucleus [adapted, with permission, from (401)]. (F) Structure of an RTN neuron whose cell body was located at the ventral surface of the medulla oblongata (in vivo recording, juxtacellular labeling with biotinamide, and transverse plane projection). Note the extensive dendrites on the ventral surface [adapted, with permission, from (300)]. (G1) Two intracellularly labeled RTN neurons recorded in a Phox2b-eGFP transgenic mouse coronal slice (green eGFP, red biotinamide). (G2) Representative acid sensitivity of one such neuron recorded at room temperature (cell attached recording, integrated rate histogram, 10 s bin) [adapted, with permission, from (231)]. (H1) RTN Phox2b+ neuron acutely isolated from a Phox2b-eGFP mouse. (H2) Acid sensitivity of such an acutely isolated RTN neuron. [adapted, with permission, from (446)]. Note that the cell responds to a change in pH, not to CO2 per se. I1, selective expression of TASK-2 potassium channels by Phox2b+ RTN neurons in mice [adapted from Gestreau et al. (137) with permission]. Left panel shows TASK-2 expression monitored with LacZ reaction product. Middle panel shows that TASK-2 expressing neurons are eliminated in a mouse line in which RTN neurons express the 27-ala Phox2b mutation and fail to develop (Task2+/−; Phox2b27Ala/+). Right panel: Task-2 expressing neurons from a Task2+/− mouse (ventral surface view) showing the superficial location in perfect register with the RTN. I2, reduced acid sensitivity of RTN neurons in Task-2 knock-out mice compared to Task-2+/− control mice [adapted, with permission, from (445)].