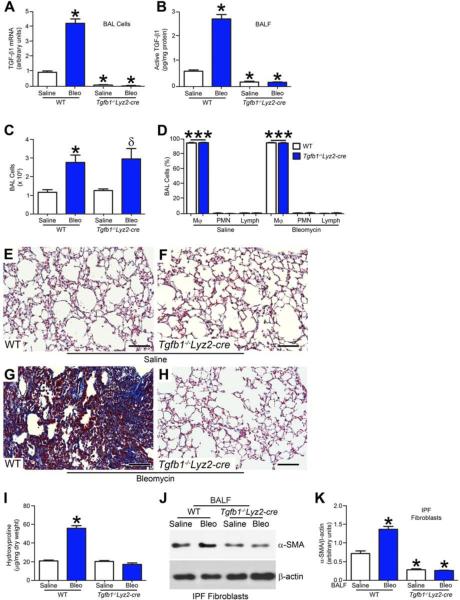
Figure 3. Macrophage-derived TGF-β1 is required for pulmonary fibrosis.
WT and Tgfb1−/− Lyz2-cre mice were exposed to saline or bleomycin intratracheally and BAL was performed 21 days later. (A) Total RNA was isolated from alveolar macrophages obtained by BAL. TGF-β1 mRNA was measured. (B) Active TGF-β1 was measured in BAL fluid by ELISA from WT and Tgfb1−/− Lyz2-cre mice; n = 6. (C) Total number of BAL cells and (D) cell differential determined using Wright-Giemsa stain from BAL; n = 6. Lungs were excised from WT and Tgfb1−/− Lyz2-cre mice exposed to (E) and (F) saline or (G) and (H) bleomycin and stained using Masson’s trichrome. Representative micrographs from WT and Tgfb1−/− Lyz2-cre mice; n = 6. Bar, 200 μm. (I) Hydroxyproline of lungs removed from WT and Tgfb1−/− Lyz2-cre mice; n = 6. (J) Immunoblot and (K) densitometry analysis of IPF fibroblasts cultured in BAL fluid from exposed WT and Tgfb1−/− Lyz2-cre mice; n = 6. *, p < 0.05 vs WT+saline; ***, p < 0.0001 vs PMN and Lymph. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s comparison. . A minumun of three independent experiments were conducted. Please see Figure S3.