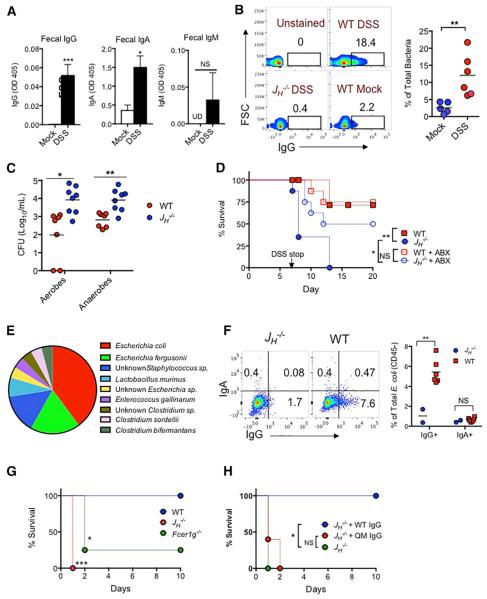
Figure 3. Gut Microbiota-Induced IgG Confers Protection against DSS-Induced Bacteremia.
(A) ELISA of fecal IgG, IgA, and IgM against fecal bacteria in feces of naive (mock) or day 7 DSS-treated mice (mock = 5 mice; day 7 DSS = 7 mice).
(B) Flow cytometry for IgG on fecal bacteria from naive (mock) or day 7 DSS-treated mice.
(C) WT and JH−/− mice were treated with DSS for 7 days and CFU of aerobes and anaerobes in the blood were determined. Each dot represents one mouse.
(D) Survival of WT and JH−/− mice, treated with or without antibiotics, after administration of 2.5% DSS in drinking water for 7 days.
(E) Percentages of bacterial isolates from spleens, livers, and blood of day 7 DSS-treated JH−/− mice.
(F) WT and JH−/− mice were i.p. injected with 5 × 107 CFU of ECM6L4 (an isolate from a DSS-treated JH−/− mouse), and E. coli was recovered from the peritoneum 6 hr after infection and analyzed for IgG or IgA coating by FACS.
(G) Survival of WT, JH−/−, and Fcer1g−/− mice after i.p. injection with 107 CFU of M6L4 (WT n = 9; JH−/− n = 8; Fcer1g−/− n = 8).
(H) Survival of untreated JH−/− mice or JH−/− mice that were administered 400 mg of purified serum IgG from WT or QM mice 24 hr prior to i.p. infection with 107 CFU of ECM6L4 (JH−/− n= 6; JH−/− +WT IgG n = 7; JH−/− +QM IgG n = 6).
Data represent two to three independent experiments. Error bars indicate SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01,
***p < 0.001. See also Figure S2.