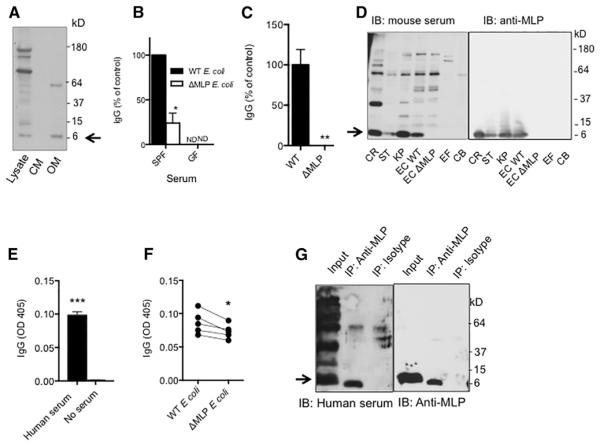
Figure 5. Gram-Negative Murein Lipoprotein Is a Major Microbiota-Derived Antigen to Induce Steady-State IgG Response.
(A) Immunoblotting for serum IgG from a 10-week-old WT naive mice that bound to E. coli total cell lysate, cytosolic membrane proteins (CM), and outer membrane proteins (OM).
(B) Reactivity of serum IgG in WT SPF or GF mice to WT or MLP-deficient E. coli (ΔMLP). Eight WT SPF mice were used; three GF mice were used.
(C) Reactivity of serum IgG in a WT SPF mouse to particles in culture supernatants from WT or ΔMLP E. coli. Eight WT SPF mice were used.
(D) Immunoblotting for IgG in the serum from a 6-week-old WT SPF mouse that bound to bacterial antigens from gram-negative C. rodentium (CR), Salmonella (ST), E. coli (EC), and K. pneumoniae (KP) and gram-positive E. faecalis (EF) and C. bifermentans (CB). Immunoblotting was performed separately for MLP using an anti-MLP monoclonal antibody.
(E) ELISA of human serum IgG against fecal bacteria (n = 5).
(F) Binding of human serum IgG to WT or MLP-deficient E. coli. Each dot represents one person.
(G) Immunoprecipitation of MLP from WT E. coli lysate by anti-MLP or isotype and immunoblotting with human serum or anti-MLP. Data represent two to three independent experiments. Error bars indicate SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. See also Figure S4.