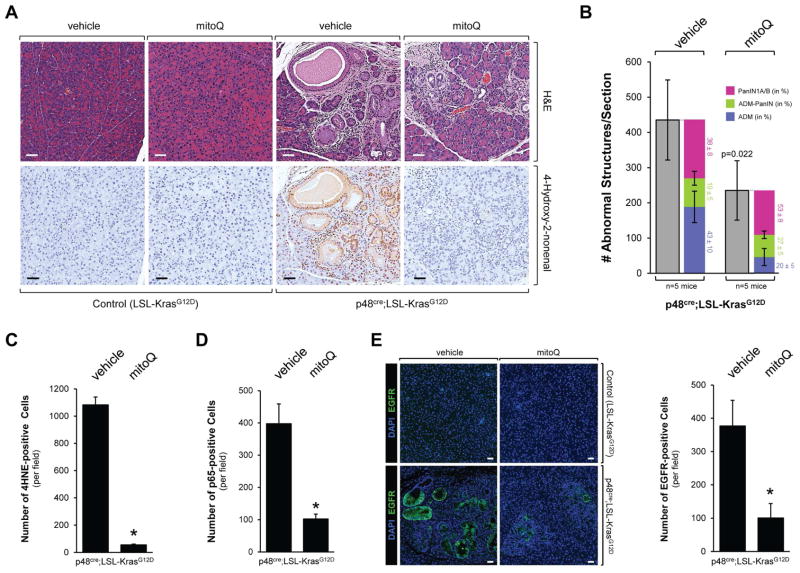
Figure 5. The mitochondrially-targeted antioxidant MitoQ decreases Kras-caused formation of pancreatic abnormal structures in vivo.
A, B: Control mice (LSL-KrasG12D) or p48cre;LSL-KrasG12D mice at an age of 3 weeks were treated with MitoQ or vehicle every other day over a time period of 12 weeks (treatment schedule shown in Supplemental Fig. S5A). At the endpoint, pancreata were analyzed by H&E staining and IHC for 4HNE as a marker for oxidative stress. A representative area of the pancreas tissue under each condition is shown in A, a quantitation of abnormal structures (and subdivision into ADM, ADM-PanIN and PanIN1A/B) per section is shown in B. Scale bar is 50 μm. * indicates statistical significance (p<0.05) as compared to vehicle-treated mice. C, D: The bar graphs show quantifications of 4HNE and p65 positive cells per field (region containing abnormal pancreatic structures). E: Samples were analyzed by immunofluorescence for expression of EGFR. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Shown is a characteristic area of the pancreas. The bar indicates 50 μm. The bar graph shows a quantification of EGFR positive cells per field (region containing abnormal pancreatic structure).