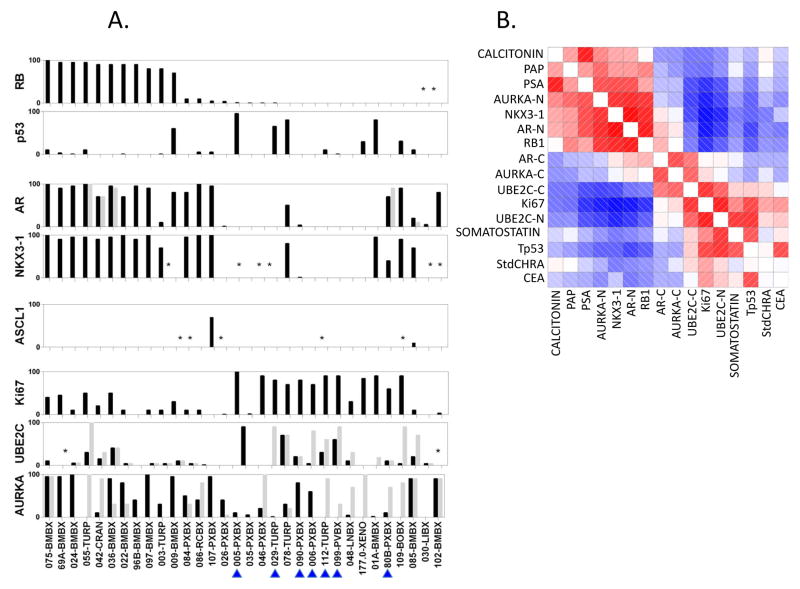
Figure 1. Immunohistochemical analysis of NCT00514540 unique “Baseline” samples.
(A) Labeling indices (% of cells staining positive for the marker listed on the y-axis, Li) for RB1, Tp53, AR, NKX3-1, AURKA, UBE2C and Ki67 in unique patient and PDX Baseline Samples (only one sample per patient is shown of the set obtained between −13 and +1 months from registration). Note, 177-0-XENO is included in the graph (n=32) but not in the analyses described in the text because the donor-patient tumor was not available for analysis. The BRN2 stains did not work and are not reported. Black bars depict nuclear staining. For AR, AURKA and UBE2C cytoplasmic stains are shown in light grey. Each individual sample is listed on the x-axis. Numbers indicate accession number on the protocol or PDX line. Letters indicate site of origin. Blue arrowheads indicate SCPC morphology. (B) Corrgram of selected tissue and serum markers among the 31 Baseline samples’ donors. Red represents positive values and blue represents negative values. The intensity of the color is proportional to the magnitude of the correlation. (*) indicate the IHC did not work. Abbreviations: RB, retinoblastoma 1; p53, tumor suppressor Tp53; NKX3-1, NK3 homeobox 1; AURKA, aurora kinase A; UBE2C, ubiquitin conjugating enzyme 2C; Ki67, antigen identified by monoclonal antibody Ki-67; RXPX, radical prostatectomy; BMBX, bone marrow biopsy; TURP, transurethral resection of prostate; CRAN, craniotomy; RCBX, rectal biopsy; XENO, xenograft; PVBX, pelvic mass biopsy; LNBX, lymph node biopsy; BOBX, bone biopsy; LIBX, liver biopsy; PAP, prostatic acid phosphatase; PSA, prostate specific antigen; -N, nuclear staining; -C, cytoplasmic staining; StdCHRA, standardized chromogranin A; CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen.