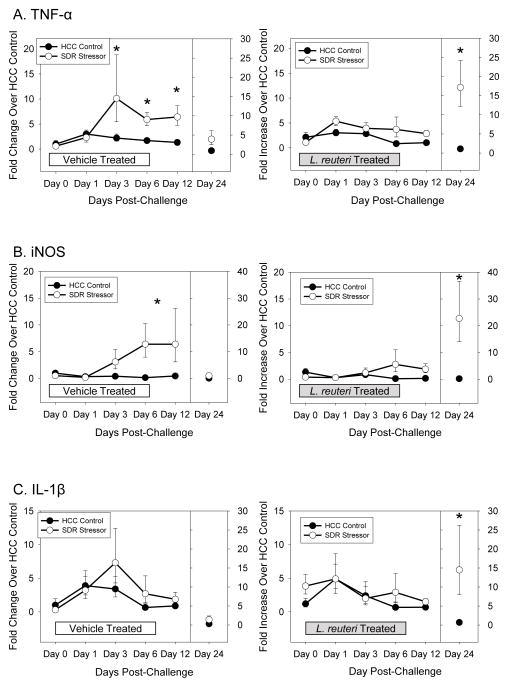
Figure 4.
Lactobacillus reuteri treatment abrogated the SDR stressor-induced increase in inflammatory cytokine and chemokine mRNA levels in the colon after C. rodentium challenge. A). Exposing mice to the SDR stressor during oral challenge with C. rodentium significantly increased TNF-α mRNA levels. Treating mice with L. reuteri prevented the increase in TNF-α until Day 24 post-challenge. B). Exposure to the SDR stressor during C. rodentium challenge increased iNOS mRNA levels. L. reuteri reduced iNOS mRNA, but stressor exposure still resulted in significant increases in iNOS. C). Exposure to the stressor during C. rodentium challenge did not increase IL-1β mRNA levels in the colon. However, mice treated with L. reuteri during exposure to the SDR stressor had elevated levels of IL-1β on Day 24 post-challenge. Data are expressed as a fold increase over uninfected (i.e., Day 0) vehicle-treated HCC control mice and are the mean ± S.E. * indicate p<.05 vs. HCC control on each individual day.