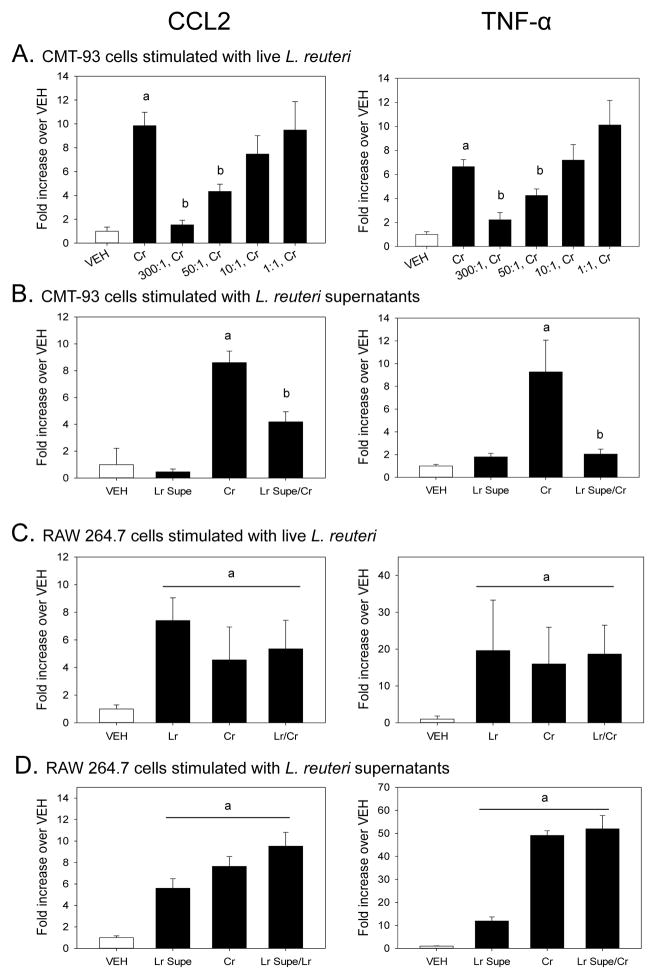
Figure 5.
Citrobacter rodentium-induced inflammatory mediator gene expression is modulated by pretreatment with live L. reuteri or its conditioned supernatants in intestinal epithelial cells, but not macrophages, in vitro. The colonic epithelial cell line, CMT-93, or RAW 264.7 macrophages were pretreated with either live, intact L. reuteri or pH-adjusted, filter sterilized L. reuteri supernatants for 1 hour prior to challenge with C. rodentium. At the end of the 2 hour pathogen challenge, total RNA was isolated in order to quantify mRNA expression by Real Time PCR. A). Epithelial CCL2 and TNF-α gene expression was significantly increased by 2 hours of C. rodentium challenge as compared to vehicle (PBS) control. Pretreatment with live L. reuteri significantly reduced C. rodentium-induced CCL2 and TNF-α mRNA expression at ratios of 300:1 and 50:1 (L. reuteri:CMT-93). a = treatment vs. VEH, p<0.005. b = Lr/Cr vs Cr, p<0.05. B). Conditioned supernatants from L. reuteri significantly reduce CCL2 and TNF-α mRNA expression in CMT-93 epithelial cells. a = treatment vs. VEH, p<0.05. b = Lr/Cr vs Cr, p<0.005. C). Live L. reuteri, C. rodentium, and L. reuteri pretreatment prior to pathogen challenge significantly enhances both CCL2 and TNF-α mRNA expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages. a = treatment vs. VEH, p<0.05. D). Conditioned supernatants also significantly enhance CCL2 and TNF-α mRNA expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages and fail to reduce C. rodentium-induced mRNA expression. a = treatment vs. VEH, p<0.001. Lr, L. reuteri treatment alone. Cr, C. rodentium treatment alone. Lr/Cr, L. reuteri pretreatment prior to C. rodentium challenge. Lr Supe, Cell-free, pH adjusted L. reuteri supernatant (5% v/v). n = 8/treatment. Data are the mean ± standard error.